对轻量级模型的需求
轻量级大语言模型模型可以让前沿的 AI 技术更加易于获取、高效、低成本。它们支持各种应用。
-
速度:由于它们的体积和复杂性得到了降低,轻量级模型通常具有更快的推理时间。这对于实时或近实时数据处理应用至关重要,如视频分析、自动驾驶汽车或推荐系统。 -
计算资源要求低:轻量级模型通常比大型模型需要更少的计算资源(如内存和处理能力)。这使它们适合部署在功能有限的设备上,如智能手机、物联网或边缘设备。 -
可扩展性:轻量级模型更容易在许多设备或用户之间扩展。这种可扩展性对于具有广泛用户基础的应用特别有利,例如移动应用。 -
成本更低:轻量级模型可以降低部署和维护人工智能系统的操作成本。它们消耗的能量更少,并且可以在更便宜的硬件上运行,使它们对企业和开发者更加易于获取、更加低成本。 -
在资源受限的环境中部署:在互联网连接不稳定或带宽有限的环境中,轻量级模型可以有效地运行,而不需要持续访问云服务。
Gemma 2
Gemma 2性能
在Gemma 2的训练过程中,采用了严格的安全协议。这包括过滤预训练数据,并在各种指标上进行全面测试,以检测和解决潜在的偏见和风险。

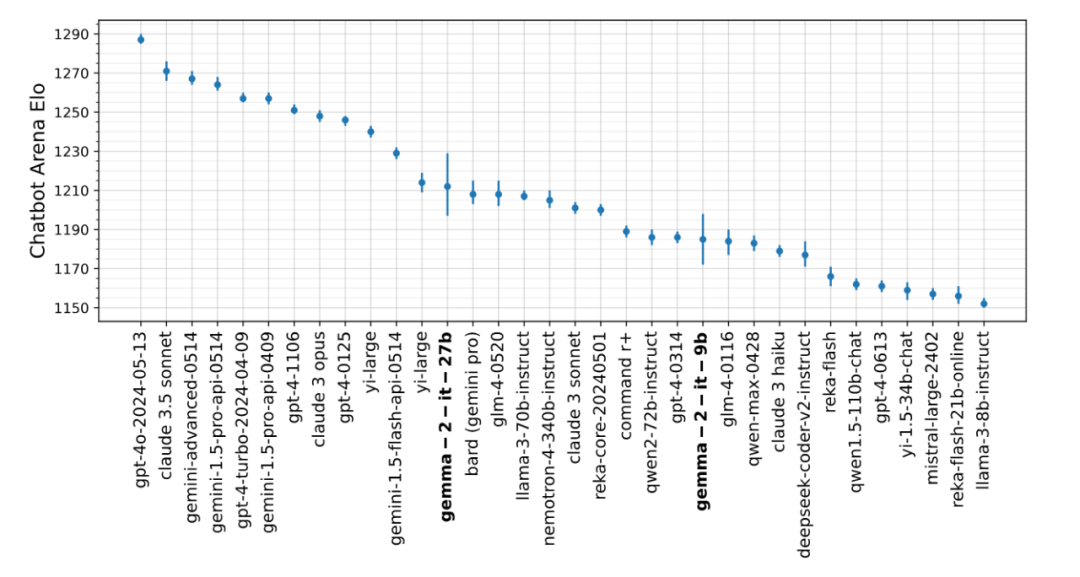
图:评估Gemma 2的9B和27B指令
上手运行:体验 Gemma 2 的强大
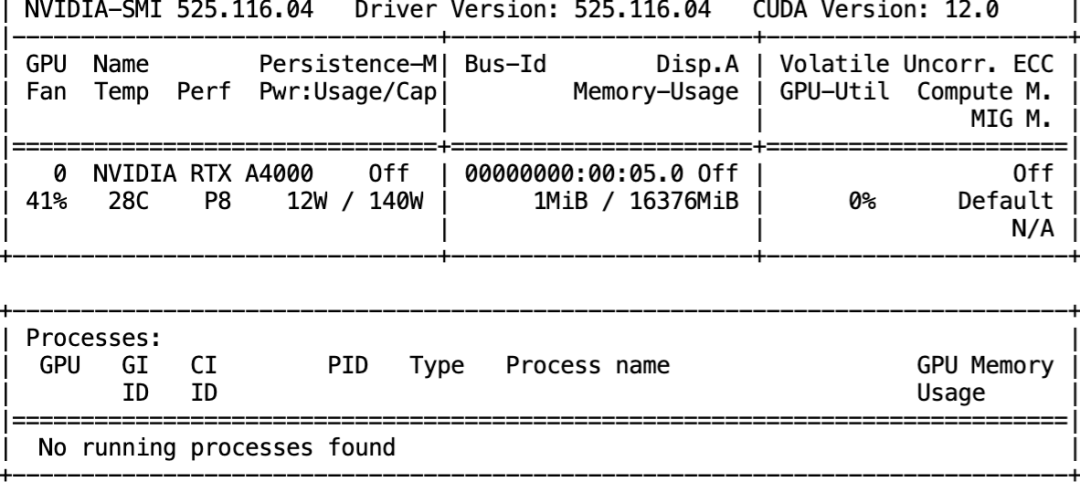
在我们开始之前,让我们收集一些关于GPU配置的信息。
nvidia-smi
ollama run gemma2
视频:运行于 Ppaperspace 的 Gemma 2模型给出的答案
我们还给了它一个编程问题:编写一个函数,通过填充空白单元格来解决数独谜题。数独谜题是一个9×9的网格,目标是填充网格,使得每一行、每一列和每个3×3的子网格都恰好包含数字1到9一次。空白单元格由字符表示。
它给出的输出是这样的:
def solveSudoku(puzzle):"""Solves a Sudoku puzzle.Args:puzzle (list): A list of strings representing the Sudoku puzzle.Returns:list: A list of strings representing the solved Sudoku puzzle."""# Iterate over the rows, columns, and subgrids.for row in range(9):for col in range(9):if puzzle[row][col] == '.':# Check if the number is already in the row, column, or subgrid.for i in range(9):if puzzle[row][i] != '.' and puzzle[i][col] != '.' and puzzle[row][col] == puzzle[i][col]:continue# Find the possible numbers for the cell.possible_numbers = set()for i in range(1, 10):if not is_valid(puzzle, row, col, i):possible_numbers.add(i)# Try each possible number.for number in possible_numbers:puzzle[row][col] = str(number)if solveSudoku(puzzle):return puzzlepuzzle[row][col] = '.'# If no solution is found, return the original puzzle.return puzzle# Helper function to check if a number is valid for a cell.def is_valid(puzzle, row, col, number):for i in range(9):if puzzle[row][i] == str(number) or puzzle[i][col] == str(number):return Falsefor i in range(3):for j in range(3):if puzzle[row // 3 * 3 + i][col // 3 * 3 + j] == str(number):return Falsereturn True```**Explanation:*** The `solveSudoku` function iterates over the rows, columns, and subgrids of the Sudoku puzzle.* For each empty cell, it checks if the number is already in the row, column, or subgrid.* It then finds the possible numbers for the cell and tries each one.* If a solution is found, it returns the solved puzzle. Otherwise, it returns the original puzzle.* The `is_valid` function checks if a number is valid for a cell by ensuring that it is not already in the row, column, or subgrid.**Example Usage:**```python# Example Sudoku puzzle.puzzle = [['5', '3', '.', '.', '7', '8', '.', '.', '.'],['.', '7', '4', '6', '.', '5', '8', '9', '.'],['.', '.', '8', '.', '9', '1', '.', '6', '.'],// ... Rest of the puzzle.]# Solve the Sudoku puzzle.solution = solveSudoku(puzzle)# Print the solved puzzle.print(solution)```


