导语:最近 GraphRAG 在社区很火,作者亲自体验后,发现了一些可以探讨和改进的地方,本文主要介绍了如何改造 GraphRAG 以支持自定义的 LLM。
01
为什么在 RAG 中引入知识图谱?
传统的 RAG 在处理复杂问题时往往表现不理想,主要是传统 RAG 未能有效捕捉实体间的复杂关系和层次结构,且通常只检索固定数量的最相关文本块:
-
缺少事情之间关系的理解:当需要关联不同信息以提供综合见解时,传统 RAG 很难将这些点连接起来。 -
缺乏整体视角:当要求 RAG 全面理解大型数据集甚至单个大型文档的整体语义概念时,缺乏宏观视角,例如,当给它一本小说并问它“这本书的主旨是什么”时,十有八九会给不出靠谱的答案。
-
这种方法适合处理需要对整个数据集进行综合理解的问题,如“数据集中的主要主题是什么?”这类问题; -
相比传统的 RAG 方法,Graph RAG 在处理全局性问题时表现出更好;

02
GraphRAG 改造计划
设计的理念很不错,但是真的去体验使用的时候,发现几个问题:
-
强依赖于 OpenAI 或 Azure 的服务。对于国内用户来说,OpenAI 的 key 还是需要国外银行卡,Azure 的 API 申请也比较繁琐,还有国外的云一般都是绑定信用卡,可能不小心用超了,上次体验 AWS 的产品,忘了删除了,后面发现扣了我快 1000 块钱,我只是体验下产品而已… -
GraphRAG 目前更像是一个 Demo 产品,想和业务结合现在也没什么可以操作的地方,肯定是需要自定义的。
-
支持自定义 LLM,OpenAI 也比较贵,换成一些更便宜的模型。我首先选择了自家的 Qwen 模型,大家可以在我的基础上扩展其他模型的支持。Qwen 默认给 50W 的 Token 使用量,够玩一段时间的,而且可以用更便宜的 turbo 模型; -
支持自定义向量数据库,方便线上使用; -
引入一些业务属性,看看如何能和业务结合在一起; -
优化下使用体验,实现生成的知识图谱可视化。
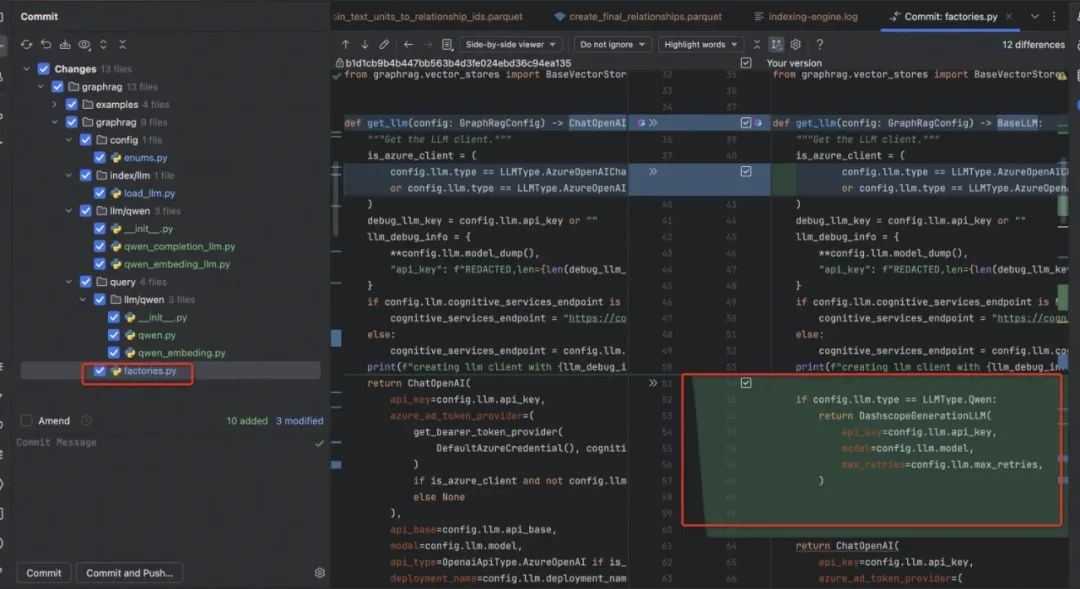
这篇文章我会首先介绍下如何改造 GraphRAG 以支持自定义的 LLM,同时我把修改 GraphRAG 的代码也开源在 GitHub 上了,也欢迎感兴趣的朋友共同建设…
03
环境准备
3.1 安装依赖
-
Python 3.10 ~ 3.12版本
git clone git@github.com:microsoft/graphrag.git
# 先安装pipx
brew install pipx
pipx ensurepath
sudo pipx ensurepath --global # optional to allow pipx actions in global scope. See "Global installation" section below.
# 安装poetry
pipx install poetry
poetry completions zsh > ~/.zfunc/_poetry
mkdir $ZSH_CUSTOM/plugins/poetry
poetry completions zsh > $ZSH_CUSTOM/plugins/poetry/_poetry
poetry install
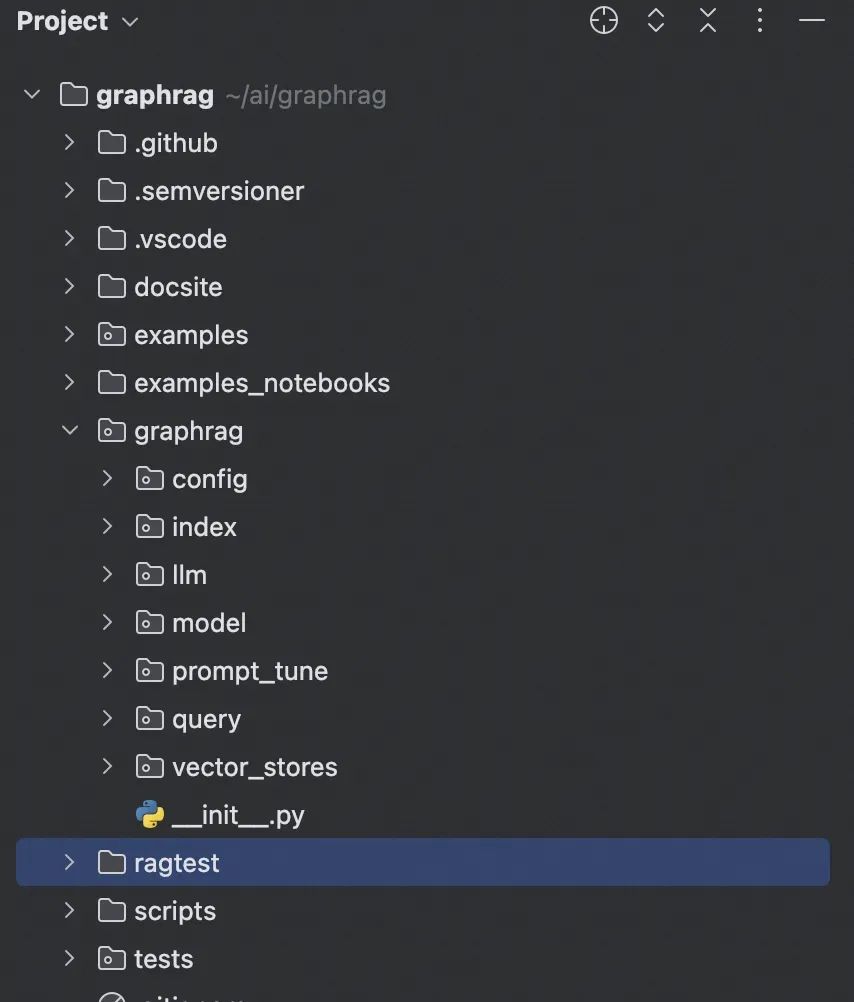
3.2 项目结构
-
config 目录:存储 GraphRAG 配置后的对象,在 GraphRAG 启动时,会读取配置文件,并将配置解析为 config 目录下的各种对象; -
index 目录:核心包,所有索引相关的核心逻辑; -
query 目录:核心包,查询相关的类和逻辑,当用户提交查询请求时,query 目录下的代码会负责解析查询、检索知识图谱、生成回答等一系列操作; -
model 目录:核心领域模型,如文本、文档、主题、关系等,GraphRAG 中的核心概念和数据结构,其他模块都围绕着这些模型进行操作和处理; -
llm 目录:支持的 LLM 的实现。如果要自定义集成通义千问,就需要在这个目录下进行实现; -
vector_stores 目录:包含向量数据库的实现。如果要自定义向量存储,需要在这个目录下进行实现。
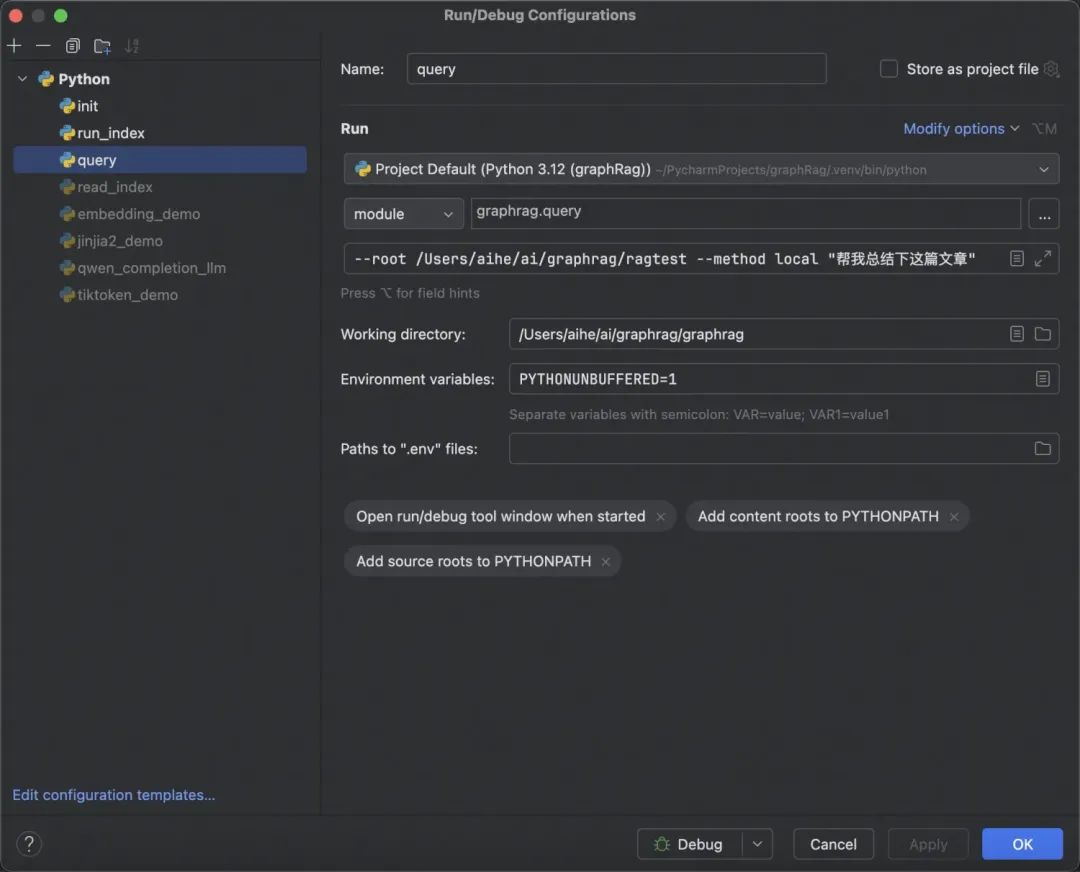
3.3 运行& Debug 项目
mkdir -p ./ragtest/input
# 这一步可以随便替换成一些其他的文档,小一点的, 这样效率比较开,可以更快的验证下我们的改造结果
curl https://www.gutenberg.org/cache/epub/24022/pg24022.txt > ./ragtest/input/book.txt
初始化项目:
python -m graphrag.index --init --root ./ragtest
对文档进行索引:
python -m graphrag.index --root ./ragtest
进行本地查询:
python -m graphrag.query
--root ./ragtest
--method local
"Who is Scrooge, and what are his main relationships?"
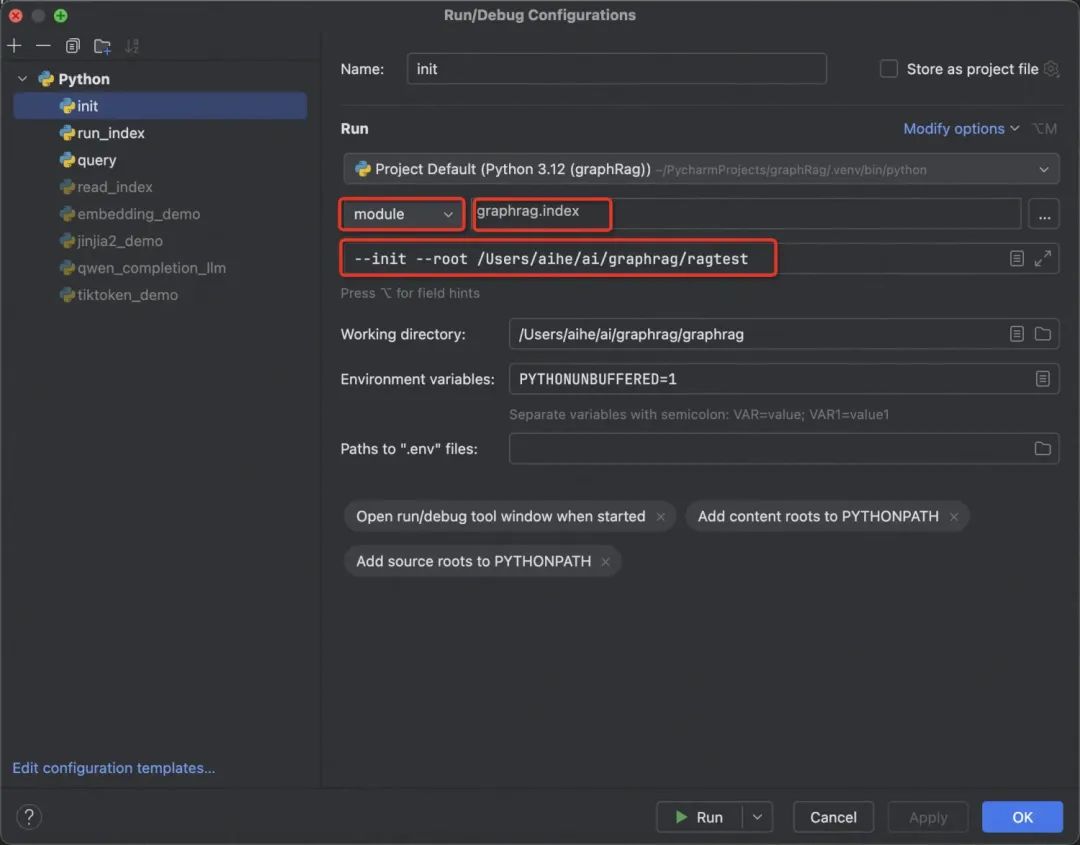
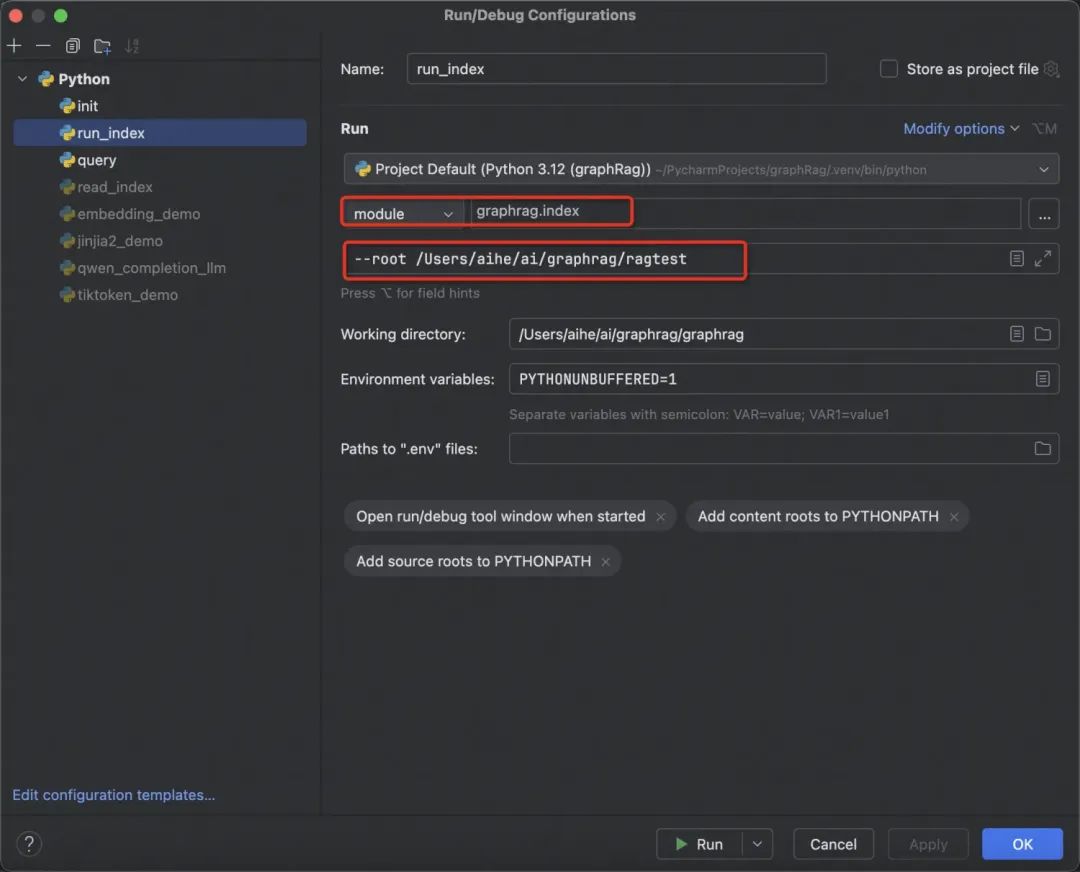
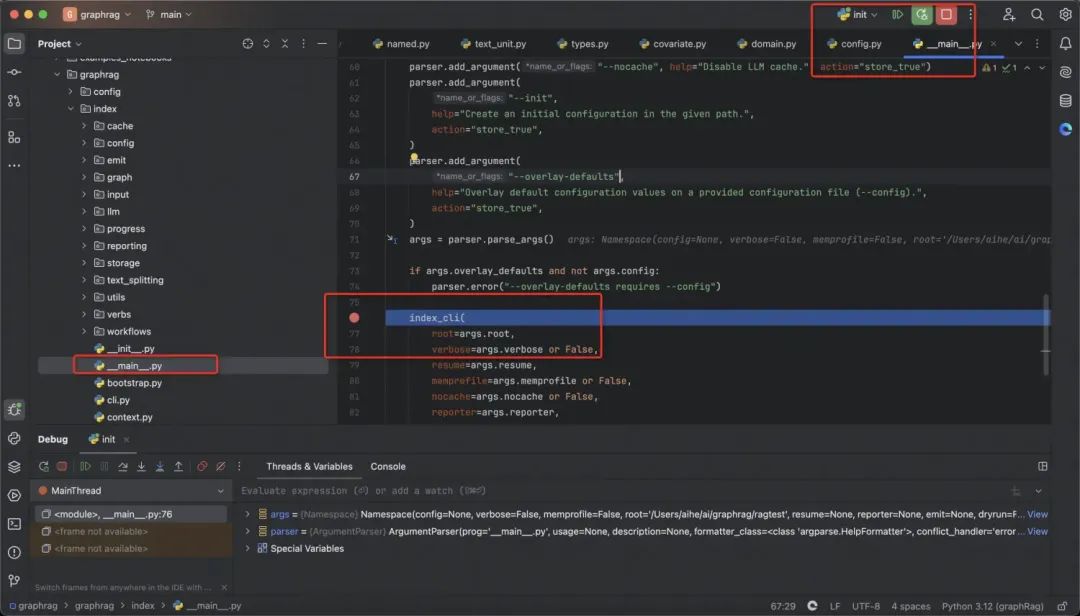
-
运行方式选择模块运行; -
模块后面参考上述官方的命令,给出的具体模块; -
接下来填具体的参数,还有工作目录不要忘了。
04
GraphRAG 支持通义千问
4.1 修改的内容
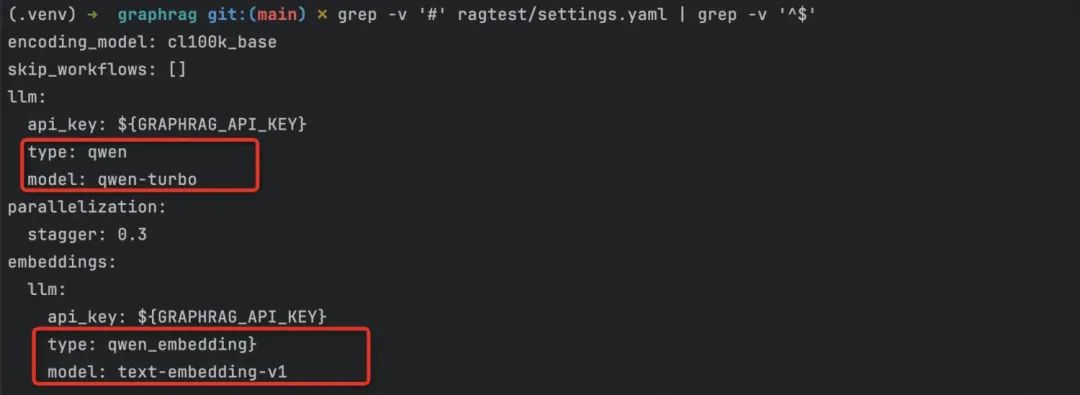
4.2 支持 Qwen 类型的配置
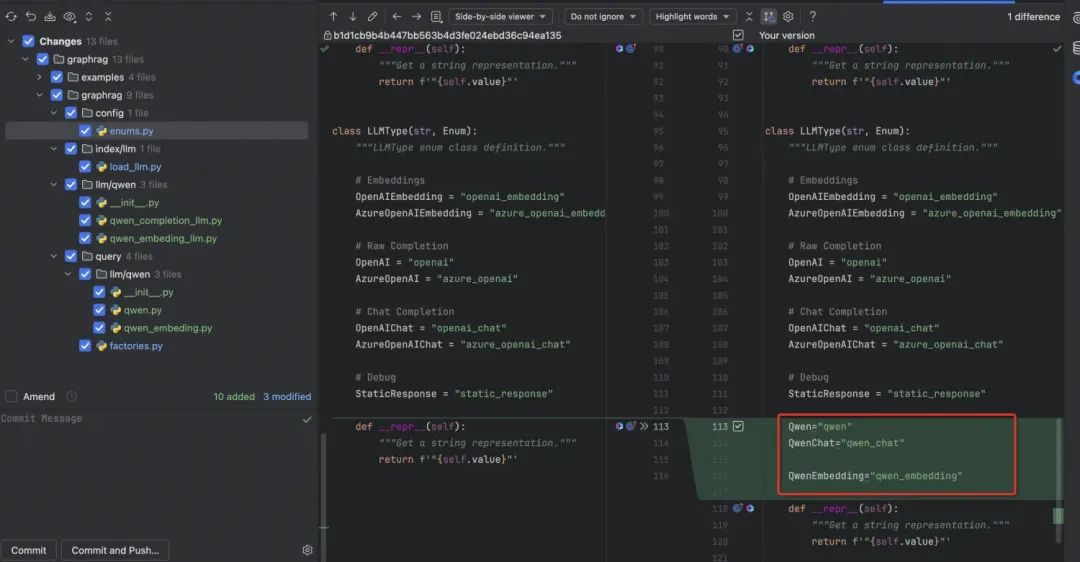
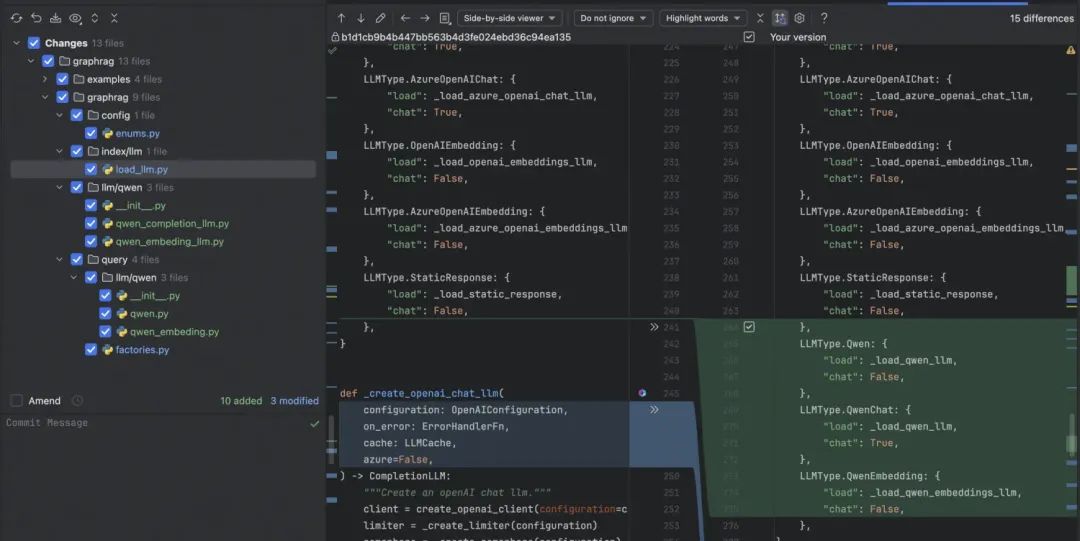
4.3 使用 Qwen 进行 Index
def _load_qwen_llm(
on_error: ErrorHandlerFn,
cache: LLMCache,
config: dict[str, Any],
azure=False,
):
log.info(f"Loading Qwen completion LLM with config {config}")
return QwenCompletionLLM(config)
def _load_qwen_embeddings_llm(
on_error: ErrorHandlerFn,
cache: LLMCache,
config: dict[str, Any],
azure=False,
):
log.info(f"Loading Qwen embeddings LLM with config {config}")
return DashscopeEmbeddingsLLM(config);
通过兼容原本的方法,到这里索引部分就可以通过 Qwen 完全进行使用了。
# Copyright (c) 2024 Microsoft Corporation.
# Licensed under the MIT License
import asyncio
import json
import logging
from http import HTTPStatus
from typing import Unpack, List, Dict
import dashscope
import regex as re
from graphrag.config import LLMType
from graphrag.llm import LLMOutput
from graphrag.llm.base import BaseLLM
from graphrag.llm.base.base_llm import TIn, TOut
from graphrag.llm.types import (
CompletionInput,
CompletionOutput,
LLMInput,
)
log = logging.getLogger(__name__)
class QwenCompletionLLM(
BaseLLM[
CompletionInput,
CompletionOutput,
]
):
def __init__(self, llm_config: dict = None):
log.info(f"llm_config: {llm_config}")
self.llm_config = llm_config or {}
self.api_key = self.llm_config.get("api_key", "")
self.model = self.llm_config.get("model", dashscope.Generation.Models.qwen_turbo)
# self.chat_mode = self.llm_config.get("chat_mode", False)
self.llm_type = llm_config.get("type", LLMType.StaticResponse)
self.chat_mode = (llm_config.get("type", LLMType.StaticResponse) == LLMType.QwenChat)
async def _execute_llm(
self,
input: CompletionInput,
**kwargs: Unpack[LLMInput],
) -> CompletionOutput:
log.info(f"input: {input}")
log.info(f"kwargs: {kwargs}")
variables = kwargs.get("variables", {})
# 使用字符串替换功能替换占位符
formatted_input = replace_placeholders(input, variables)
if self.chat_mode:
history = kwargs.get("history", [])
messages = [
*history,
{"role": "user", "content": formatted_input},
]
response = self.call_with_messages(messages)
else:
response = self.call_with_prompt(formatted_input)
if response.status_code == HTTPStatus.OK:
if self.chat_mode:
return response.output["choices"][0]["message"]["content"]
else:
return response.output["text"]
else:
raise Exception(f"Error {response.code}: {response.message}")
def call_with_prompt(self, query: str):
print("call_with_prompt {}".format(query))
response = dashscope.Generation.call(
model=self.model,
prompt=query,
api_key=self.api_key
)
return response
def call_with_messages(self, messages: list[dict[str, str]]):
print("call_with_messages {}".format(messages))
response = dashscope.Generation.call(
model=self.model,
messages=messages,
api_key=self.api_key,
result_format='message',
)
return response
# 主函数
async def _invoke_json(self, input: TIn, **kwargs) -> LLMOutput[TOut]:
try:
output = await self._execute_llm(input, **kwargs)
except Exception as e:
print(f"Error executing LLM: {e}")
return LLMOutput[TOut](output=None, json=None)
# 解析output的内容
extracted_jsons = extract_json_strings(output)
if len(extracted_jsons) > 0:
json_data = extracted_jsons[0]
else:
json_data = None
try:
output_str = json.dumps(json_data)
except (TypeError, ValueError) as e:
print(f"Error serializing JSON: {e}")
output_str = None
return LLMOutput[TOut](
output=output_str,
json=json_data
)
def replace_placeholders(input_str, variables):
for key, value in variables.items():
placeholder = "{" + key + "}"
input_str = input_str.replace(placeholder, value)
return input_str
def preprocess_input(input_str):
# 预处理输入字符串,移除或转义特殊字符
return input_str.replace('<', '<').replace('>', '>')
def extract_json_strings(input_string: str) -> List[Dict]:
# 正则表达式模式,用于匹配 JSON 对象
json_pattern = re.compile(r'({(?:[^{}]|(?R))*})')
# 查找所有匹配的 JSON 子字符串
matches = json_pattern.findall(input_string)
json_objects = []
for match in matches:
try:
# 尝试解析 JSON 子字符串
json_object = json.loads(match)
json_objects.append(json_object)
except json.JSONDecodeError:
# 如果解析失败,忽略此子字符串
log.warning(f"Invalid JSON string: {match}")
pass
return json_objects
实现下对应的 Embeding 模型;
"""The EmbeddingsLLM class."""
import logging
log = logging.getLogger(__name__)
from typing import Unpack
from graphrag.llm.base import BaseLLM
from graphrag.llm.types import (
EmbeddingInput,
EmbeddingOutput,
LLMInput,
)
from http import HTTPStatus
import dashscope
import logging
log = logging.getLogger(__name__)
class QwenEmbeddingsLLM(BaseLLM[EmbeddingInput, EmbeddingOutput]):
"""A text-embedding generator LLM using Dashscope's API."""
def __init__(self, llm_config: dict = None):
log.info(f"llm_config: {llm_config}")
self.llm_config = llm_config or {}
self.api_key = self.llm_config.get("api_key", "")
self.model = self.llm_config.get("model", dashscope.TextEmbedding.Models.text_embedding_v1)
async def _execute_llm(
self, input: EmbeddingInput, **kwargs: Unpack[LLMInput]
) -> EmbeddingOutput:
log.info(f"input: {input}")
response = dashscope.TextEmbedding.call(
model=self.model,
input=input,
api_key=self.api_key
)
if response.status_code == HTTPStatus.OK:
res = [embedding["embedding"] for embedding in response.output["embeddings"]]
return res
else:
raise Exception(f"Error {response.code}: {response.message}")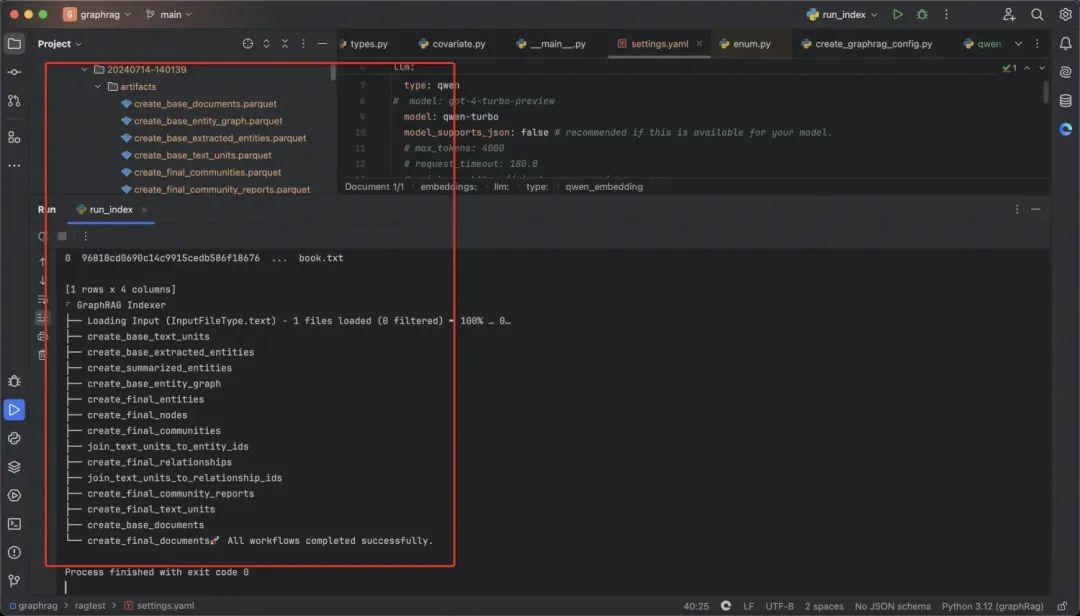
4.4 使用 Qwen 进行 Query
-
query 相比 index 支持了流式的输出内容:
import asyncio
import logging
from http import HTTPStatus
from typing import Any
import dashscope
from tenacity import (
Retrying,
RetryError,
retry_if_exception_type,
stop_after_attempt,
wait_exponential_jitter,
)
from graphrag.query.llm.base import BaseLLMCallback, BaseLLM
from graphrag.query.progress import StatusReporter, ConsoleStatusReporter
log = logging.getLogger(__name__)
class DashscopeGenerationLLM(BaseLLM):
def __init__(
self,
api_key: str | None = None,
model: str | None = None,
max_retries: int = 10,
request_timeout: float = 180.0,
retry_error_types: tuple[type[BaseException]] = (Exception,),
reporter: StatusReporter = ConsoleStatusReporter(),
):
self.api_key = api_key
self.model = model or dashscope.Generation.Models.qwen_turbo
self.max_retries = max_retries
self.request_timeout = request_timeout
self.retry_error_types = retry_error_types
self._reporter = reporter
def generate(
self,
messages: str | list[str],
streaming: bool = False,
callbacks: list[BaseLLMCallback] | None = None,
**kwargs: Any,
) -> str:
try:
retryer = Retrying(
stop=stop_after_attempt(self.max_retries),
wait=wait_exponential_jitter(max=10),
reraise=True,
retry=retry_if_exception_type(self.retry_error_types),
)
for attempt in retryer:
with attempt:
return self._generate(
messages=messages,
streaming=streaming,
callbacks=callbacks,
**kwargs,
)
except RetryError as e:
self._reporter.error(
message="Error at generate()", details={self.__class__.__name__: str(e)}
)
return ""
else:
return ""
async def agenerate(
self,
messages: str | list[str],
streaming: bool = False,
callbacks: list[BaseLLMCallback] | None = None,
**kwargs: Any,
) -> str:
try:
retryer = Retrying(
stop=stop_after_attempt(self.max_retries),
wait=wait_exponential_jitter(max=10),
reraise=True,
retry=retry_if_exception_type(self.retry_error_types),
)
for attempt in retryer:
with attempt:
return await asyncio.to_thread(
self._generate,
messages=messages,
streaming=streaming,
callbacks=callbacks,
**kwargs,
)
except RetryError as e:
self._reporter.error(f"Error at agenerate(): {e}")
return ""
else:
return ""
def _generate(
self,
messages: str | list[str],
streaming: bool = False,
callbacks: list[BaseLLMCallback] | None = None,
**kwargs: Any,
) -> str:
if isinstance(messages, list):
response = dashscope.Generation.call(
model=self.model,
messages=messages,
api_key=self.api_key,
stream=streaming,
incremental_output=streaming,
timeout=self.request_timeout,
result_format='message',
**kwargs,
)
else:
response = dashscope.Generation.call(
model=self.model,
prompt=messages,
api_key=self.api_key,
stream=streaming,
incremental_output=streaming,
timeout=self.request_timeout,
**kwargs,
)
# if response.status_code != HTTPStatus.OK:
# raise Exception(f"Error {response.code}: {response.message}")
if streaming:
full_response = ""
for chunk in response:
if chunk.status_code != HTTPStatus.OK:
raise Exception(f"Error {chunk.code}: {chunk.message}")
decoded_chunk = chunk.output.choices[0]['message']['content']
full_response += decoded_chunk
if callbacks:
for callback in callbacks:
callback.on_llm_new_token(decoded_chunk)
return full_response
else:
if isinstance(messages, list):
return response.output["choices"][0]["message"]["content"]
else:
return response.output["text"]
实现 Query 的 Embedding 对象:
import asyncio
import logging
from typing import Any
import dashscope
from tenacity import (
Retrying,
RetryError,
retry_if_exception_type,
stop_after_attempt,
wait_exponential_jitter,
)
from graphrag.query.llm.base import BaseTextEmbedding
from graphrag.query.progress import StatusReporter, ConsoleStatusReporter
log = logging.getLogger(__name__)
class DashscopeEmbedding(BaseTextEmbedding):
def __init__(
self,
api_key: str | None = None,
model: str = dashscope.TextEmbedding.Models.text_embedding_v1,
max_retries: int = 10,
retry_error_types: tuple[type[BaseException]] = (Exception,),
reporter: StatusReporter = ConsoleStatusReporter(),
):
self.api_key = api_key
self.model = model
self.max_retries = max_retries
self.retry_error_types = retry_error_types
self._reporter = reporter
def embed(self, text: str, **kwargs: Any) -> list[float]:
try:
embedding = self._embed_with_retry(text, **kwargs)
return embedding
except Exception as e:
self._reporter.error(
message="Error embedding text",
details={self.__class__.__name__: str(e)},
)
return []
async def aembed(self, text: str, **kwargs: Any) -> list[float]:
try:
embedding = await asyncio.to_thread(self._embed_with_retry, text, **kwargs)
return embedding
except Exception as e:
self._reporter.error(
message="Error embedding text asynchronously",
details={self.__class__.__name__: str(e)},
)
return []
def _embed_with_retry(self, text: str, **kwargs: Any) -> list[float]:
try:
retryer = Retrying(
stop=stop_after_attempt(self.max_retries),
wait=wait_exponential_jitter(max=10),
reraise=True,
retry=retry_if_exception_type(self.retry_error_types),
)
for attempt in retryer:
with attempt:
response = dashscope.TextEmbedding.call(
model=self.model,
input=text,
api_key=self.api_key,
**kwargs,
)
if response.status_code == 200:
embedding = response.output["embeddings"][0]["embedding"]
return embedding
else:
raise Exception(f"Error {response.code}: {response.message}")
except RetryError as e:
self._reporter.error(
message="Error at embed_with_retry()",
details={self.__class__.__name__: str(e)},
)
return []
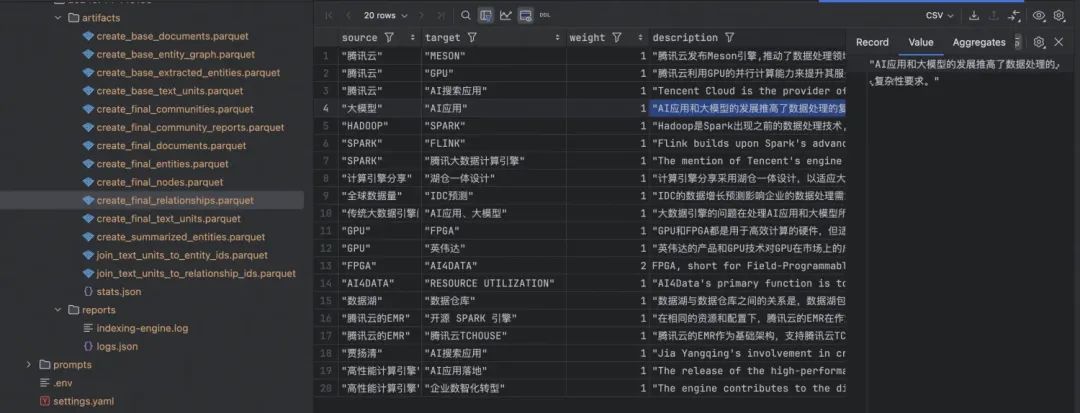
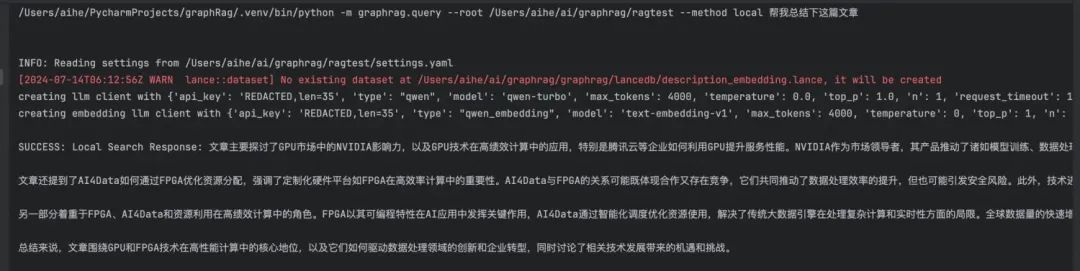
运行下 Query 的效果:
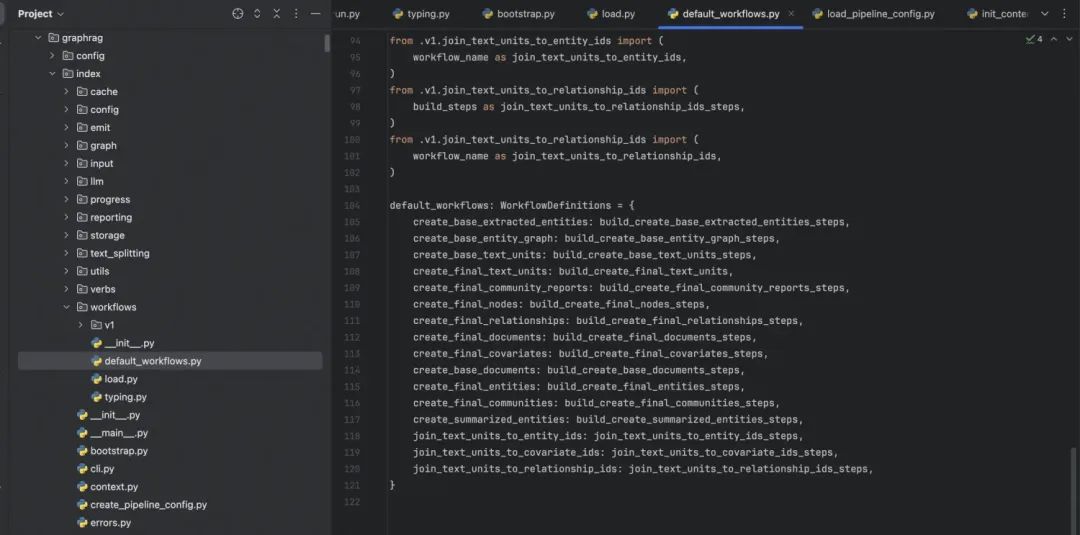
4.5 项目中的一些关键节点
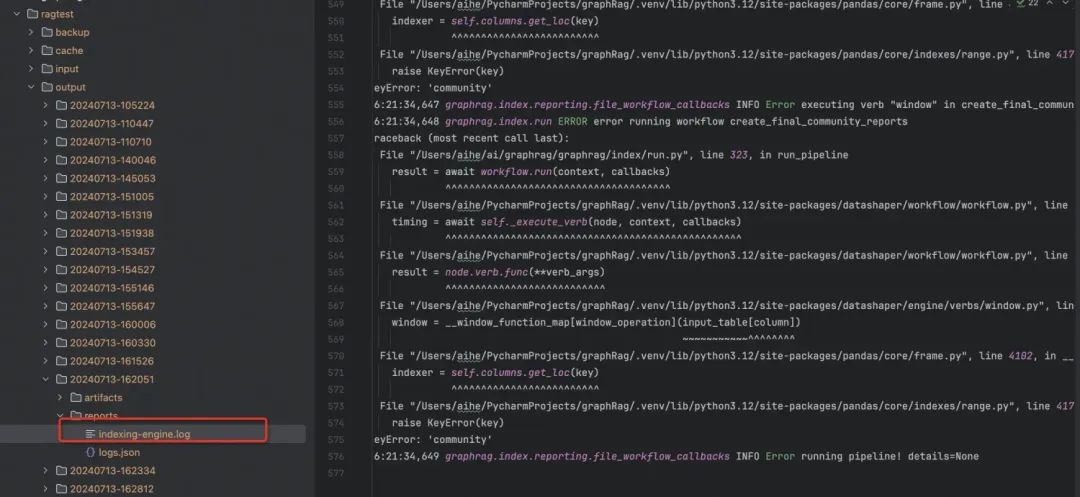
4.6 遇到错误怎么办
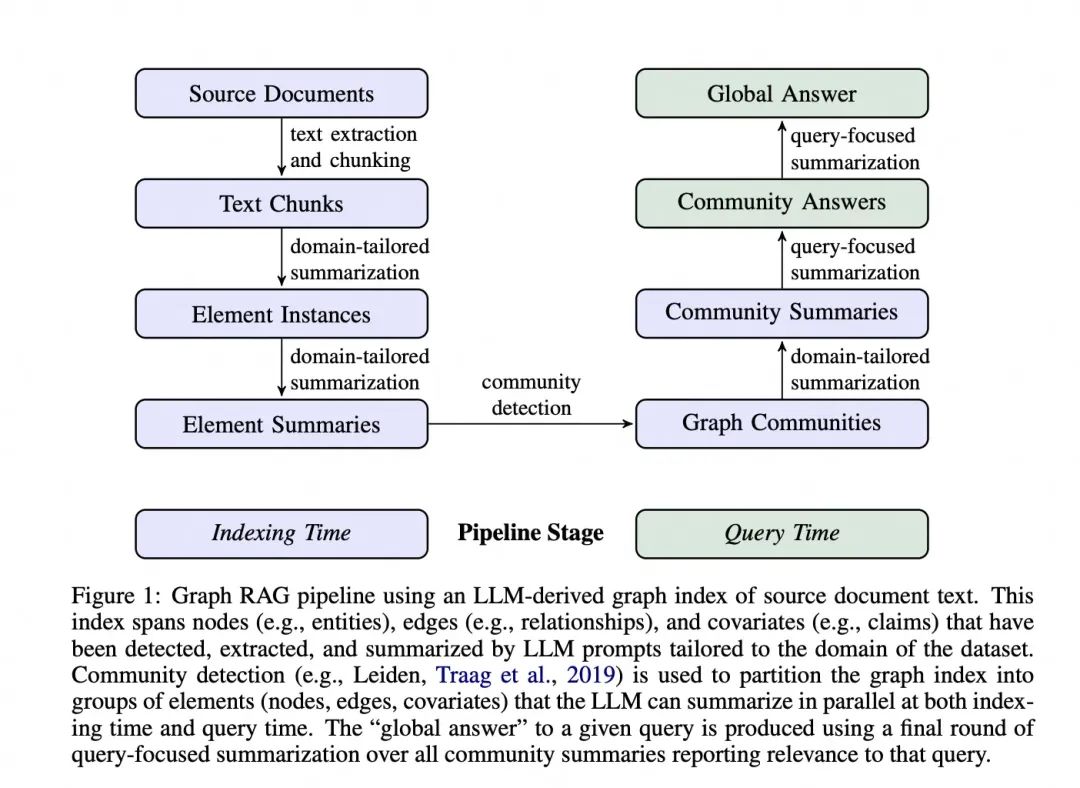
05
GraphRAG 的核心步骤
-
"Gleaning" 是一种迭代式的信息提取方法。初始提取: LLM 首先对文本块进行一次实体和关系提取。评估:LLM 被要求评估是否所有实体都被提取出来了。迭代提取::如果 LLM 认为有遗漏,它会被提示进行额外的"gleaning"轮次,尝试提取之前可能遗漏的实体。多轮进行:这个过程可以重复多次,直到达到预设的最大轮次或 LLM 认为没有更多实体可提取。
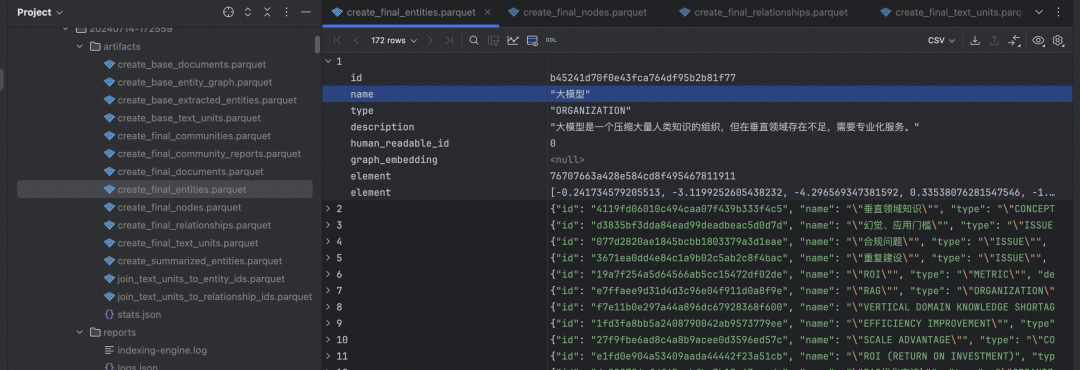
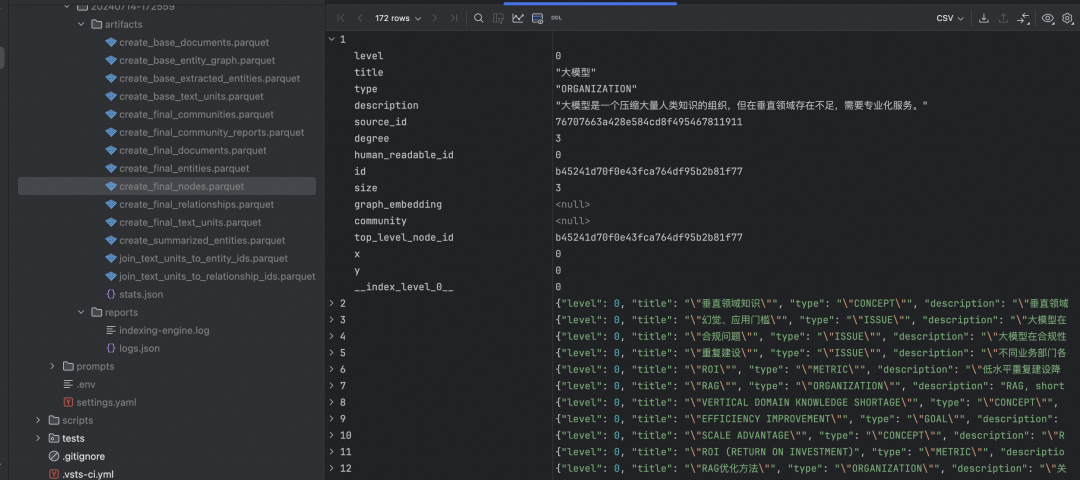
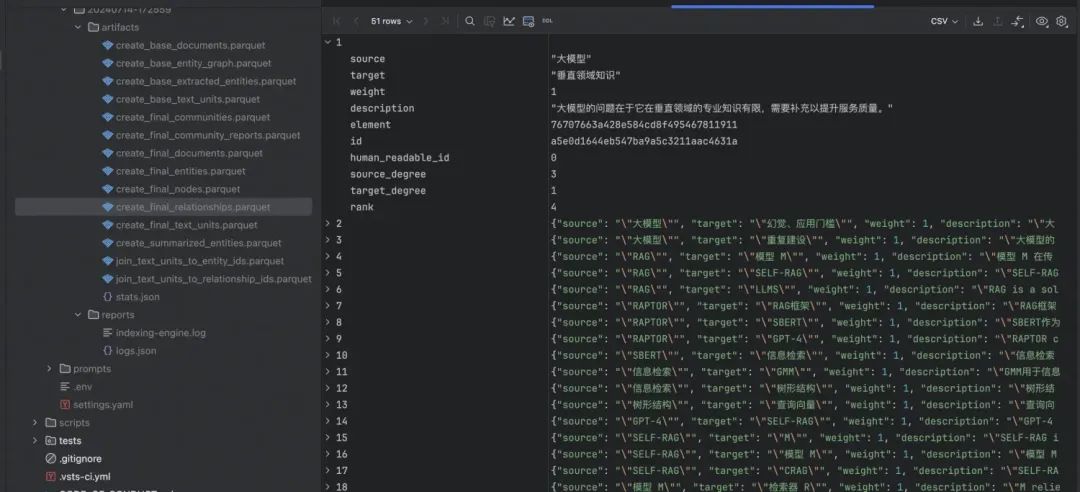
-
使用 Leiden 算法进行检测,得到层次化的社区结构,Leiden 算法帮助我们把大量的文本信息组织成有意义的群组,使得我们可以更容易地理解和处理这些信息。
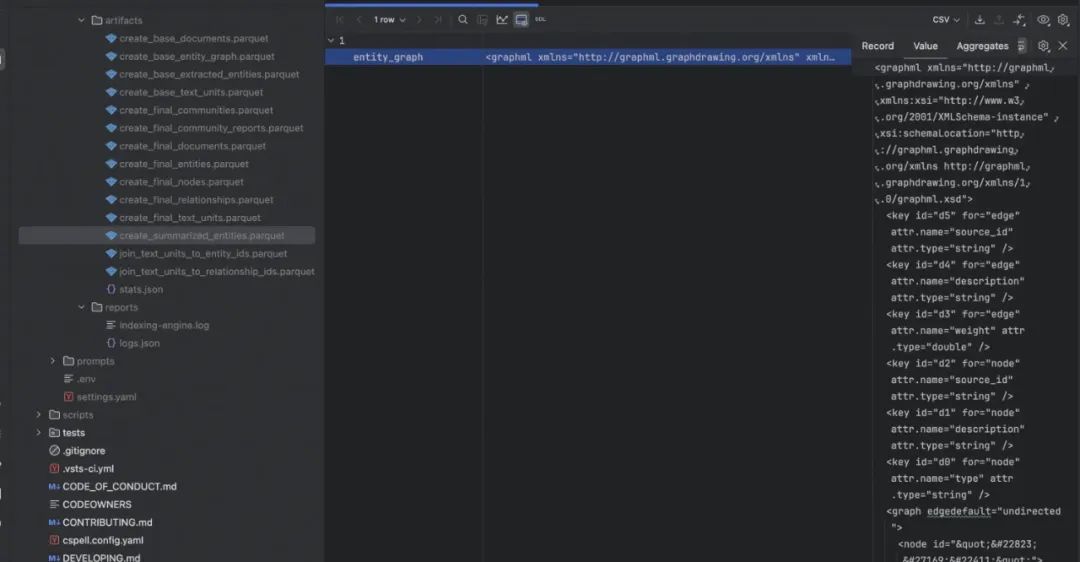
-
为每个社区生成报告式摘要; -
对于叶子级社区,直接总结其包含的所有元素; -
对于高层社区,递归地利用子社区摘要。
-
Community Summaries(社区摘要):预先生成的,包含了图中每个社区(即相关实体群组)的概要信息。它们存储了关于每个主题领域的关键信息,通过问题找到一些相关的主题(社区摘要); -
Community Answers(社区回答):当收到用户查询时,系统会并行处理每个社区摘要,对每个社区摘要,系统会生成一个针对用户问题的部分答案,系统还会给每个部分答案评分,表示其对回答问题的相关性; -
Global Answer:系统会收集所有有用的部分答案(过滤掉评分为0的答案),然后,它会按照相关性评分对这些答案进行排序。最后,系统会综合这些部分答案,生成一个全面、连贯的最终答案。
06
小结
-
自定义 VectorStore 实现 -
GraphRAG 可视化过程 -
业务集成 GraphRAG


