-
✨ 精确评估与排名:通过排行榜查看经过严格评估前后的 LLM 最新排名。 -
✨ 预生成样本:BigCodeBench 通过开源多种模型生成的 LLM 代码样本,加速了代码智能研究——无需重新运行成本高昂的基准测试!
-
执行环境:BigCodeBench 的执行环境相较于 EvalPlus 约束更少,以支持具有多样化库依赖的任务。 -
测试评估:BigCodeBench 依赖于 unittest 来评估生成的代码,这更适合于 BigCodeBench 中的测试框架。

BigCodeBench 为每个任务提供了复杂且以用户为中心的指导,包括清晰的功能描述、输入/输出格式、错误处理以及经过验证的交互示例。该平台避免使用逐步任务指导,相信有能力的 LLMs 应该能够从用户的角度以开放式的方式理解和解决任务。通过测试用例来验证特定功能。
# We elaborate the above task with some test cases:# Requirements SetUpimport unittestfrom unittest.mock import patchimport http.clientimport sslimport socket# Start the testclass TestCases(unittest.TestCase):# Mock the successful connection and assess the response content@patch('http.client.HTTPSConnection')def test_response_content(self, mock_conn):""" Test the content of the response. """mock_conn.return_value.getresponse.return_value.read.return_value = b'Expected Content'result = task_func('www.example.com', 443, '/content/path')self.assertEqual(result, 'Expected Content')# Mock the failed connection and assess the error handling@patch('socket.create_connection')@patch('http.client.HTTPSConnection')def test_ssl_handshake_error_handling(self, mock_conn, mock_socket):""" Test handling of SSL handshake errors. """mock_socket.side_effect = ssl.SSLError('SSL handshake failed')with self.assertRaises(ssl.SSLError):task_func('badssl.com', 443, '/test/path')# More test cases...
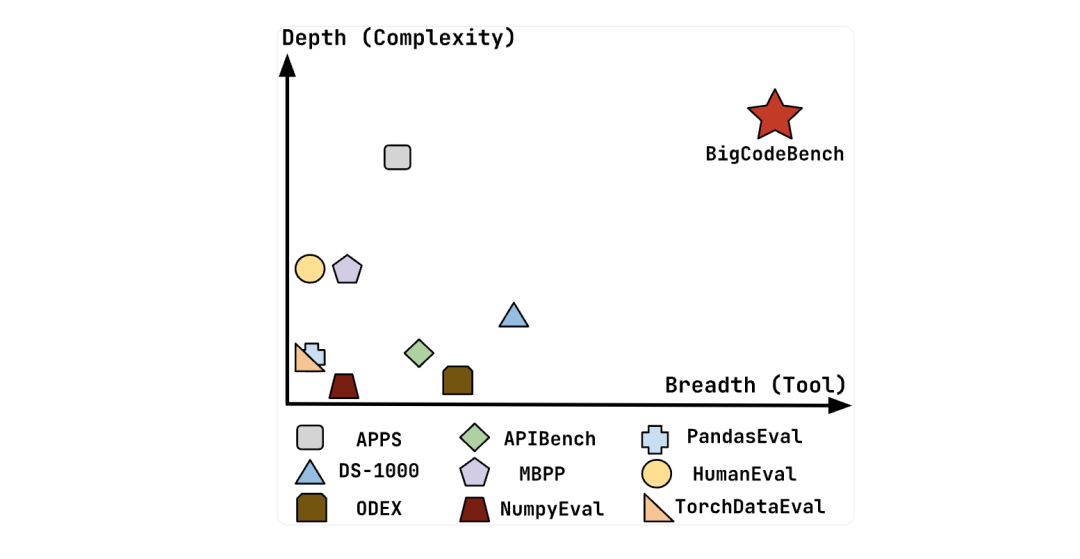
为了深入理解实现的复杂性以及工具使用的多样性,BigCodeBench 与包括 APPS、DS-1000、ODEX、APIBench、MBPP、NumpyEval、PandasEval、HumanEval 和 TorchDataEval 等代表性基准测试中的任务进行了比较。结果显示,BigCodeBench 在实现全面功能方面需要更复杂的推理和问题解决能力。
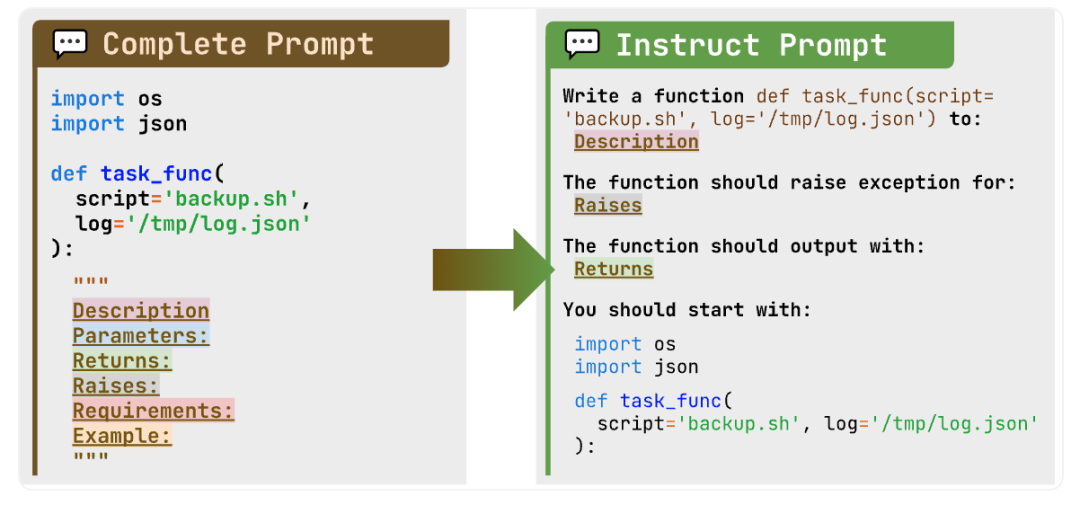
如图中所示的任务,主要目标场景是代码补全(标记为 BigCodeBench-Complete),在此场景中,LLMs 需要根据文档字符串中详细的指令完成函数的实现。然而,考虑到下游应用,例如多轮对话,用户可能会以更会话化、更简洁的方式描述需求。这正是经过指令调整的 LLMs 显示出优势的地方,因为它们被训练以遵循自然语言指令并相应生成代码片段。为了测试模型是否真正理解人类的意图并将其转化为代码,我们创建了 BigCodeBench-Instruct,这是一个更具挑战性的 BigCodeBench 变体,旨在评估经过指令调整的 LLMs。
开始之前,请先设置环境:
# Install to use bigcodebench.evaluatepip install bigcodebench --upgrade# If you want to use the evaluate locally, you need to install the requirementspip install -I -r https://raw.githubusercontent.com/bigcode-project/bigcodebench/main/Requirements/requirements-eval.txt# Install to use bigcodebench.generate# You are strongly recommended to install the generate dependencies in a separate environmentpip install bigcodebench[generate] --upgrade
建议使用flash-attn来生成代码示例。
pip install -U flash-attn
要从模型生成代码示例,可以使用以下命令:
bigcodebench.generate --model [model_name] --subset [complete|instruct] --greedy --bs [bs] --temperature [temp] --n_samples [n_samples] --resume --backend [vllm|hf|openai|mistral|anthropic|google] --tp [gpu_number] [--trust_remote_code] [--base_url [base_url]]
生成的代码样本将存储在一个名为 [model_name]–bigcodebench-[instruct|complete]–[backend]-[temp]-[n_samples].jsonl 的文件中。或者,可以使用以下命令来利用我们预先构建的 Docker 镜像来生成代码样本:
# If you are using GPUsdocker run --gpus '"device=$CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES"' -v $(pwd):/app -t bigcodebench/bigcodebench-generate:latest--model [model_name]--subset [complete|instruct][--greedy]--bs [bs]--temperature [temp]--n_samples [n_samples]--resume--backend [vllm|hf|openai|mistral|anthropic|google]--tp [gpu_number]# ...Or if you are using CPUsdocker run -v $(pwd):/app -t bigcodebench/bigcodebench-generate:latest--model [model_name]--subset [complete|instruct][--greedy]--bs [bs]--temperature [temp]--n_samples [n_samples]--resume--backend [vllm|hf|openai|mistral|anthropic|google]
# If you wish to use gated or private HuggingFace models and datasetsdocker run -e HUGGING_FACE_HUB_TOKEN=$token -v $(pwd):/app -t bigcodebench/bigcodebench-generate:latest # omit other arguments4# Similarly, to use other backends that require authenticationdocker run -e OPENAI_API_KEY=$OPENAI_API_KEY -v $(pwd):/app -t bigcodebench/bigcodebench-generate:latest # omit other argumentsdocker run -e GOOGLE_API_KEY=$OPENAI_API_KEY -v $(pwd):/app -t bigcodebench/bigcodebench-generate:latest # omit other argumentsdocker run -e ANTHROPIC_KEY=$ANTHROPIC_KEY -v $(pwd):/app -t bigcodebench/bigcodebench-generate:latest # omit other arguments
LLM 生成的文本可能无法包含自然语言行或不完整的额外代码的可编译代码。我们提供了一个名为 bigcodebench.sanitize 的工具来清理代码:
# ? If you want to get the calibrated results:bigcodebench.sanitize --samples samples.jsonl --calibrate# Sanitized code will be produced to `samples-sanitized-calibrated.jsonl`# ? If you want to get the original results:bigcodebench.sanitize --samples samples.jsonl# Sanitized code will be produced to `samples-sanitized.jsonl`# ? If you are storing codes in directories:bigcodebench.sanitize --samples /path/to/vicuna-[??]b_temp_[??]# Sanitized code will be produced to `/path/to/vicuna-[??]b_temp_[??]-sanitized`
强烈建议您使用沙箱,例如docker:
# Mount the current directory to the containerdocker run -v $(pwd):/app bigcodebench/bigcodebench-evaluate:latest --subset [complete|instruct] --samples samples-sanitized-calibrated# ...Or locally ⚠️bigcodebench.evaluate --subset [complete|instruct] --samples samples-sanitized-calibrated# ...If the ground truth is working locally (due to some flaky tests)bigcodebench.evaluate --subset [complete|instruct] --samples samples-sanitized-calibrated --no-gt
-
多语言支持:目前,BigCodeBench 仅支持 Python 语言,并且难以扩展至其他编程语言。鉴于函数调用通常与特定语言绑定,在非 Python 语言中寻找具有相同功能的包或库存在挑战。 -
严谨性:尽管 BigCodeBench 在真实解决方案上实现了高测试覆盖率,但这并不足以保证所有由 LLMs 生成的代码解决方案都能正确地根据现有测试用例进行评估。先前的研究如 EvalPlus 尝试通过利用 LLM 和变异策略来增加输入输出对,以扩展有限的测试用例。然而,将 EvalPlus 适配到 BigCodeBench 的测试框架中面临挑战。EvalPlus 着重于输入输出断言,而 BigCodeBench 中的大多数测试框架在运行时检查预期程序行为时需要进行非平凡的配置(例如,模拟补丁)。 -
泛化能力:关键问题在于模型对未见工具和任务的泛化能力如何。目前,BigCodeBench 覆盖了常用库和日常编程任务。在基准测试中使用新兴库如 transformers 和 langchain 对模型进行评估将更具吸引力。 -
演化性:库可能会变得过时或更新,这意味着模型训练所用的源代码数据将持续演变。模型可能不会记忆已弃用的库版本的函数调用,这对于任何依赖工具的编程基准测试来说,要正确评估模型能力而不进行定期更新是一个挑战。另一个相关问题是,由于训练数据的演变,测试集可能会受到污染。 -
交互性:近期的研究兴趣集中在将 LLMs 作为代理的概念上,这被视为通向人工通用智能的一条路径。具体来说,LLMs 将在一个较少约束的沙盒环境中运行,它们可以与网络浏览器和终端等应用程序进行交互。这种环境有助于发掘自我调试和自我反思等能力。