word2vec 是一种广泛用于自然语言处理的技术,主要目的是将单词转换为词向量(将单词表示为数字向量)。这些词向量能够反映不同词语的相似性,使得语义上或语法上相近的词语在向量空间中也相互接近。

word2vec 是自然语言处理领域的一种基础技术,广泛应用于文本分析、机器翻译、情感分析等多种场景。
word2vec 的工作原理
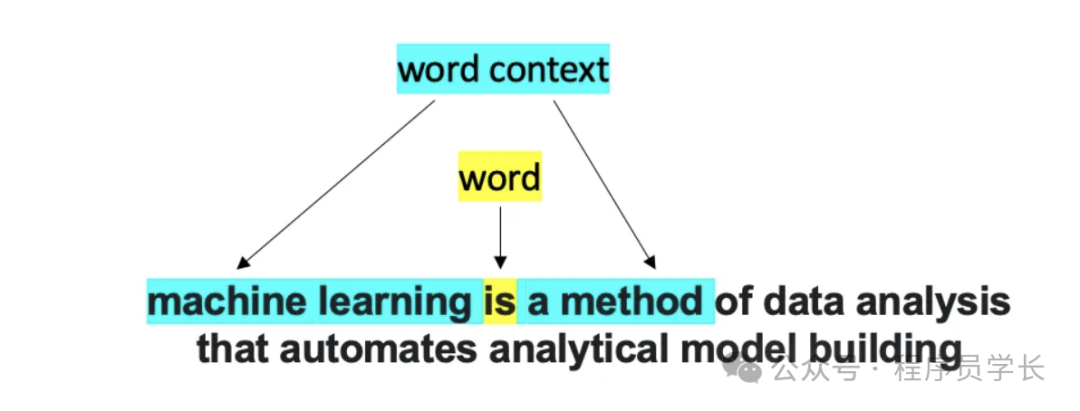
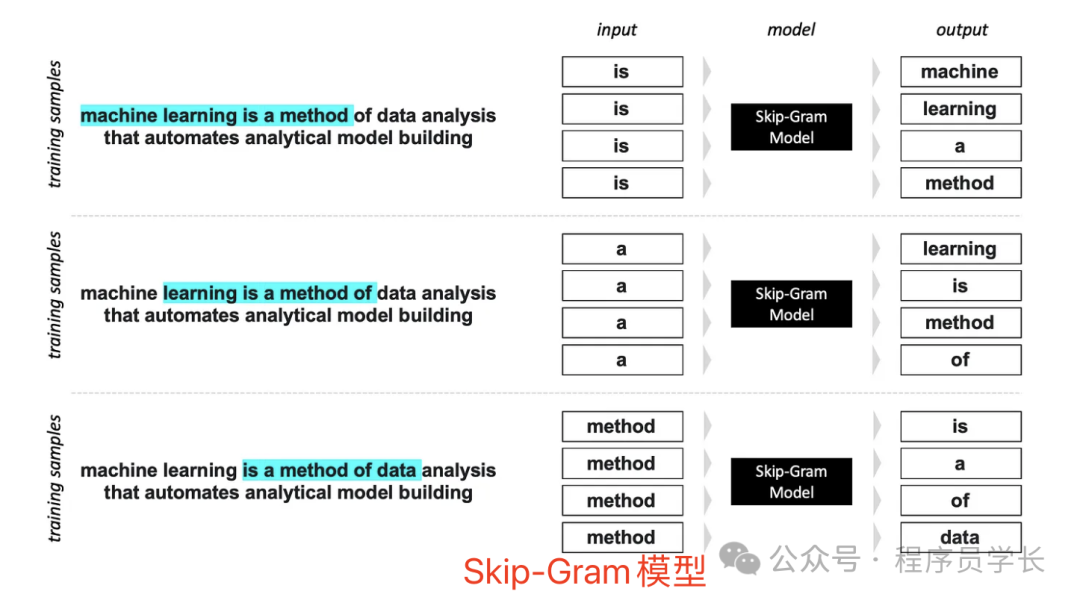
如下图所示,其中 N 为 2,对于单词 word,它的上下文词为 machine、learning、 a 和 method。
-
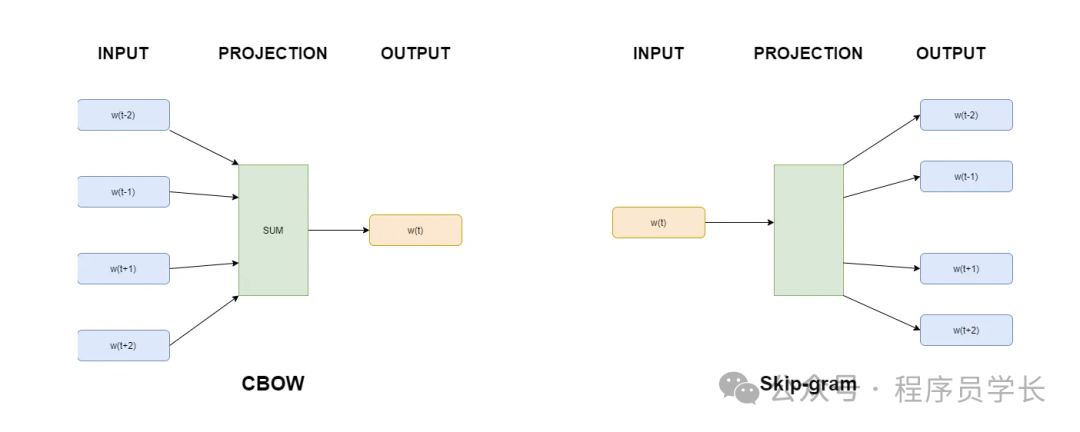
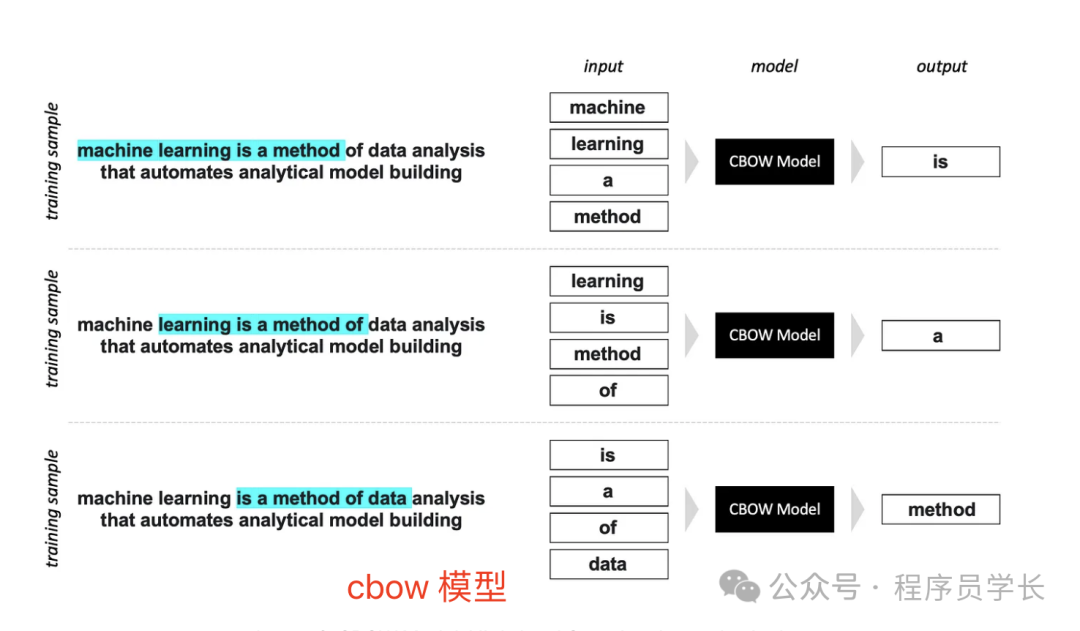
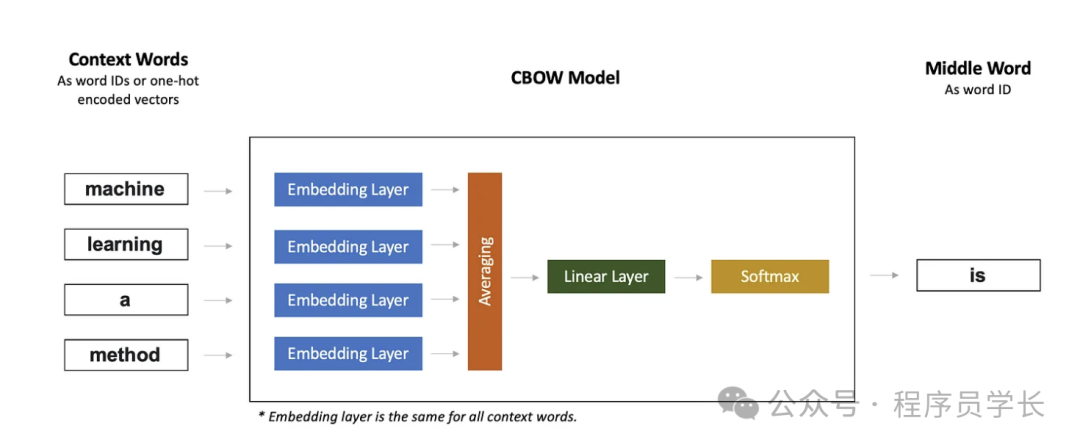
CBOW(连续词袋模型),一种根据上下文词预测当前词的模型。
-
Skip-Gram,一种根据当前单词预测上下文单词的模型。
下面,我们来看一下具体的模型架构。
-
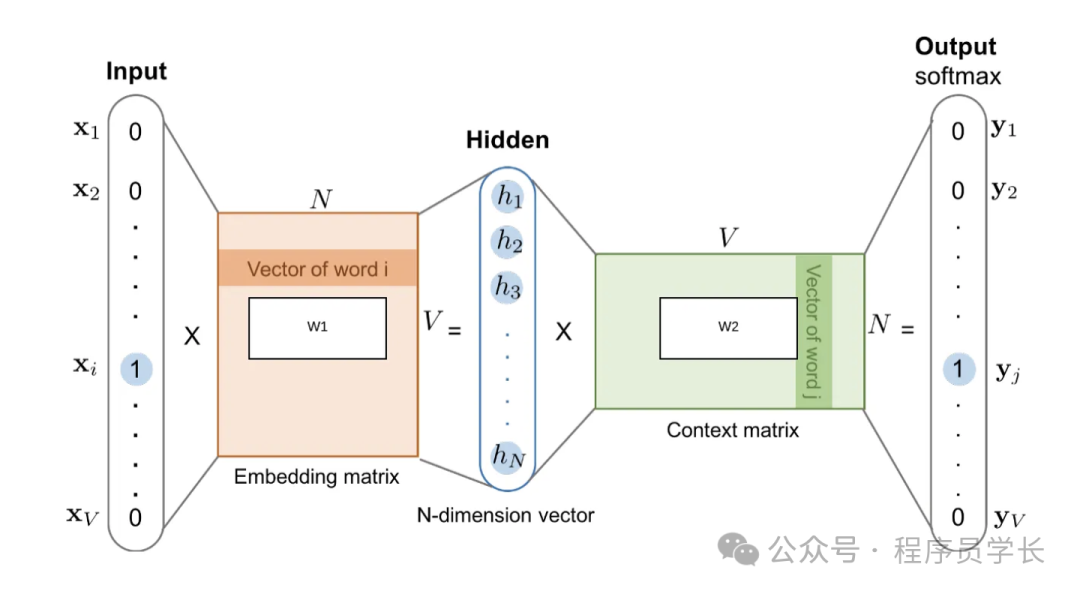
输入层
模型的输入为单词对应的 one-hot 编码。 其中 CBOW 模型的输入是某个目标词周围的上下文单词的 one-hot 编码。而 Skip-gram 模型的输入是目标词的 one-hot 编码。 -
隐藏层
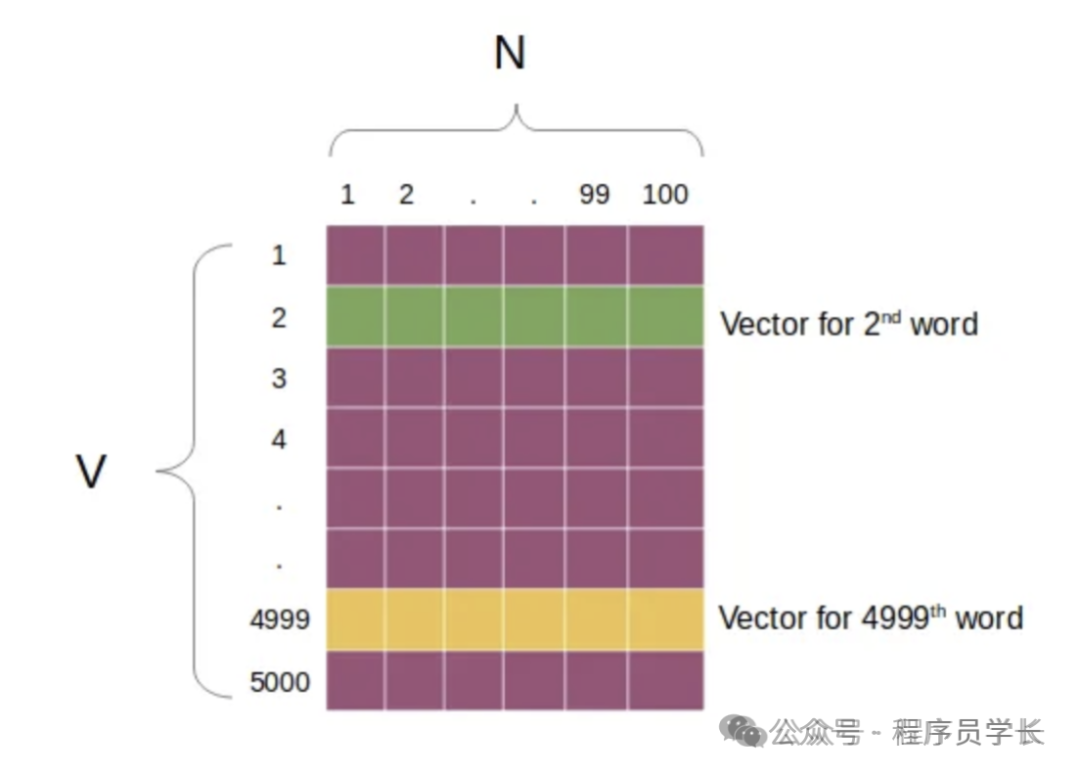
输入层直接连接到隐藏层(通过权重矩阵),没有非线性激活函数。隐藏层的输出是当前单词的词向量表示。 -
输出层
接下来是具有 Softmax 激活的线性层。
CBOW 和 Skip-Gram 模型的区别在于输入词的数量。CBOW 模型采用多个词,每个词经过相同的嵌入层,然后对词嵌入向量进行平均,然后进入线性层。而 Skip-Gram 模型则采用单个词。
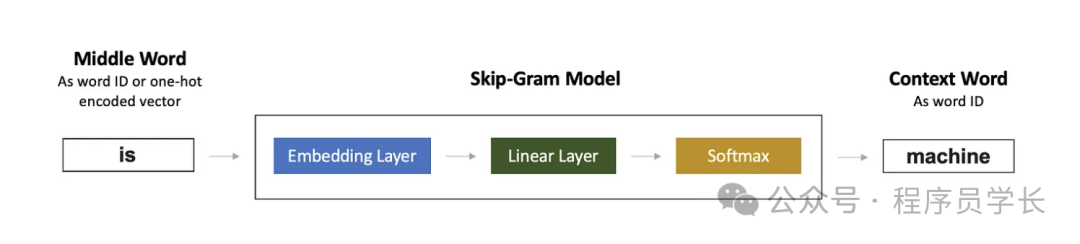
Skip-Gram 模型的前向传播过程详解
Skip-Gram 模型的前向传播过程详解
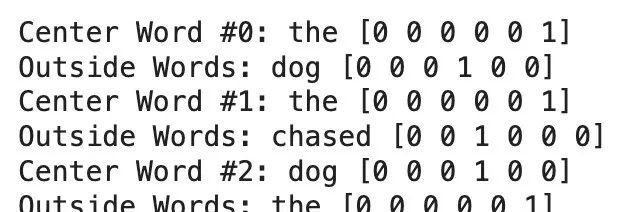
对中心词和外部词进行编码
此中心词和相应外部词将用于训练模型。
-
import re
import numpy as np
WINDOW_SIZE = 2
def create_vocabulary ( training_data ):
""" 通过标记训练数据返回排序后的单词列表。"""
all_words = ' ' .join(training_data).lower()
all_words = all_words.replace( '.' , '' )
all_words = all_words.split( ' ' )
vocab = list ( set (all_words))
vocab.sort()
return vocab
def one_hot(word, vocab, vocab_size ):
""" 返回单词的独热编码向量。"""
one_hot = [0]*vocab_size
pos = vocab.index(word)
one_hot[pos] = 1
one_hot = np.array(one_hot)
return one_hot
def create_vector_word_map (vocab, vocab_size ):
""" 返回一个词典映射,将独热向量转换回单词。"""
vec_to_word = { str (one_hot(word, vocab, vocab_size)): word for word in vocab}
return vec_to_word
def encode_training_data(training_data, vocab_size, window_size):
""" Encode the center and outside words as one-hot vectors."""
encoded_training_data = []
for sentence in training_data:
# Tokenize the sentence
tokens = re.sub(r'[^ws]', '', sentence).lower().split(' ')
# Encode each center word and its surrounding context words
for word_pos, word in enumerate(tokens):
center_word = one_hot(word, vocab, vocab_size)
for outside_pos in range(word_pos-window_size,
word_pos+window_size+1):
if (outside_pos >= 0) and (outside_pos < len(tokens))
and (outside_pos != word_pos):
outside_word=one_hot(tokens[outside_pos],
vocab,
vocab_size)
encoded_training_data.append([center_word, outside_word])
return encoded_training_data
def print_training_encodings(encoded_training_data, vocab, vec_to_word):
""" Print the encodings for each (center word - outside words) set."""
max_len = len(max(vocab, key=len))
for num, (cw_vector, ow_vectors) in enumerate(encoded_training_data):
cw = vec_to_word[str(cw_vector)]
ow = vec_to_word[str(ow_vectors)]
print(f'Center Word #{num}: {cw} {cw_vector}')
print(f'Outside Words: {ow} {ow_vectors}')
# Create training data
training_data = ['The dog chased the cat around the garden.']
# Encode training data
vocab = create_vocabulary(training_data)
vocab_size = len(vocab)
vec_to_word = create_vector_word_map(vocab, vocab_size)
encoded_training_data = encode_training_data(training_data,
vocab_size,
window_size=WINDOW_SIZE)
# # Print out results
print_training_encodings(encoded_training_data, vocab, vec_to_word)
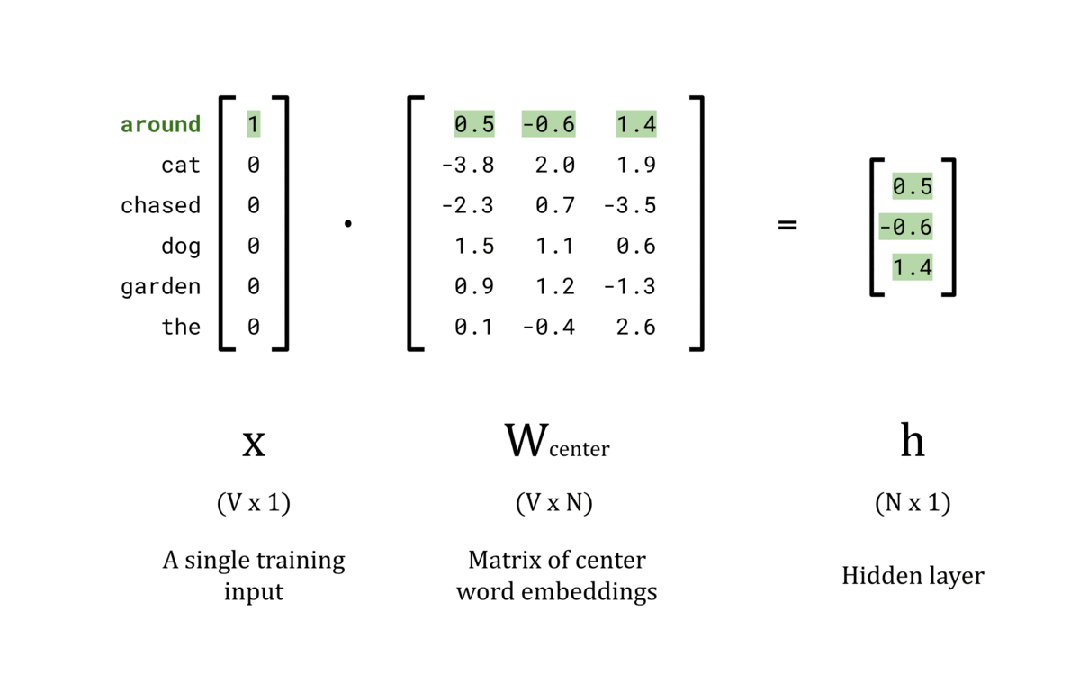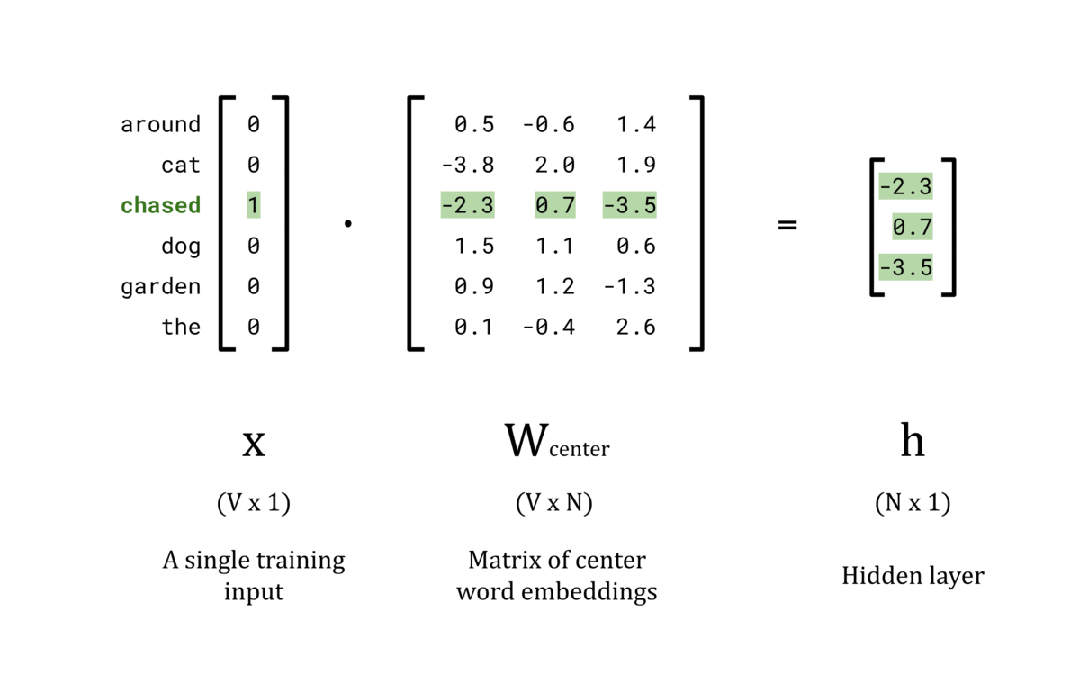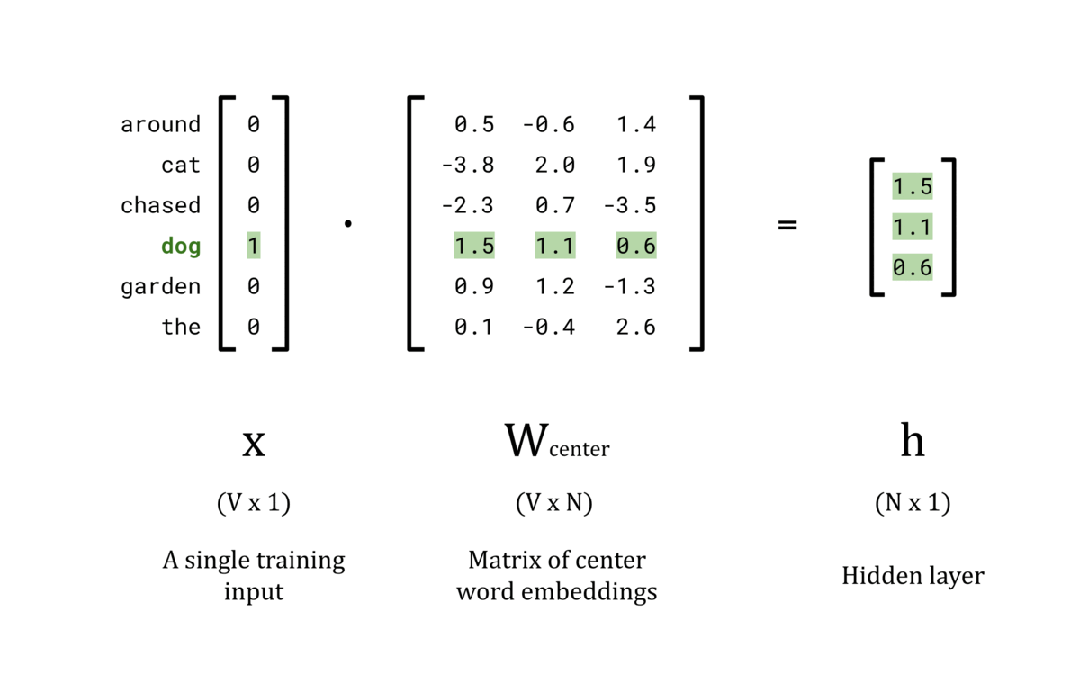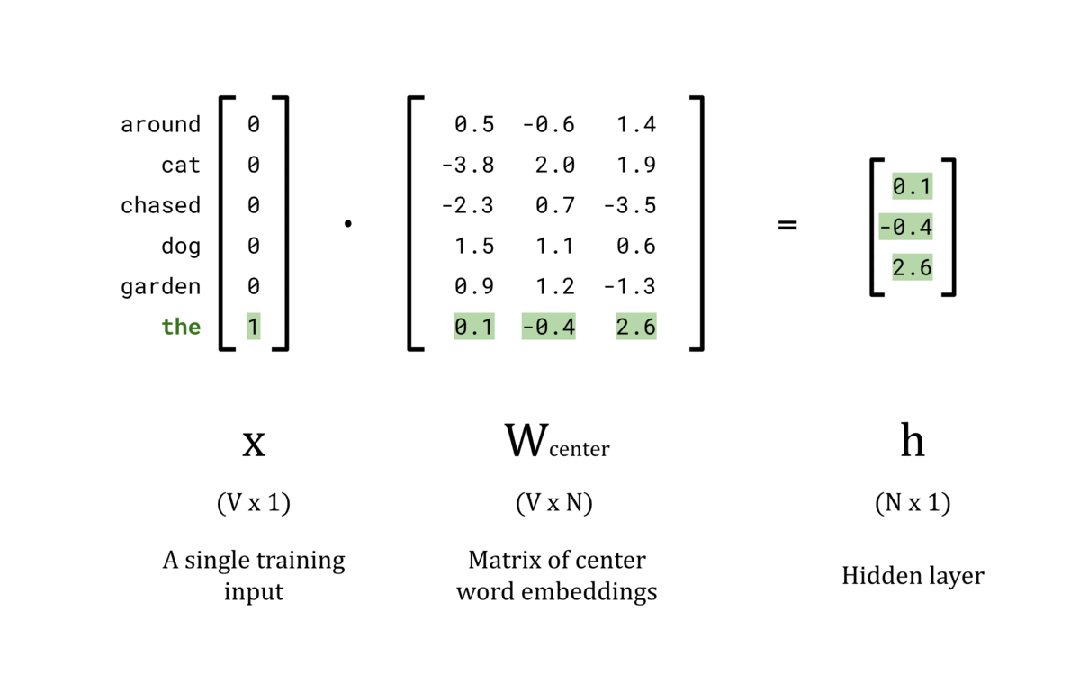
EMBEDDING_DIM = 3
# Calculate the hidden layer vector
x = encoded_training_data[0][0]
w_center = np.random.rand(vocab_size, EMBEDDING_DIM)
h = np.dot(x, w_center)
# Print the results
print(f'Center word, w(t): {vec_to_word[str(x)]}n')
print(f'Input vector, x: {x}n')
print(f'W_center: nn{w_center}n')
print(f'Hidden layer, h: {h}n')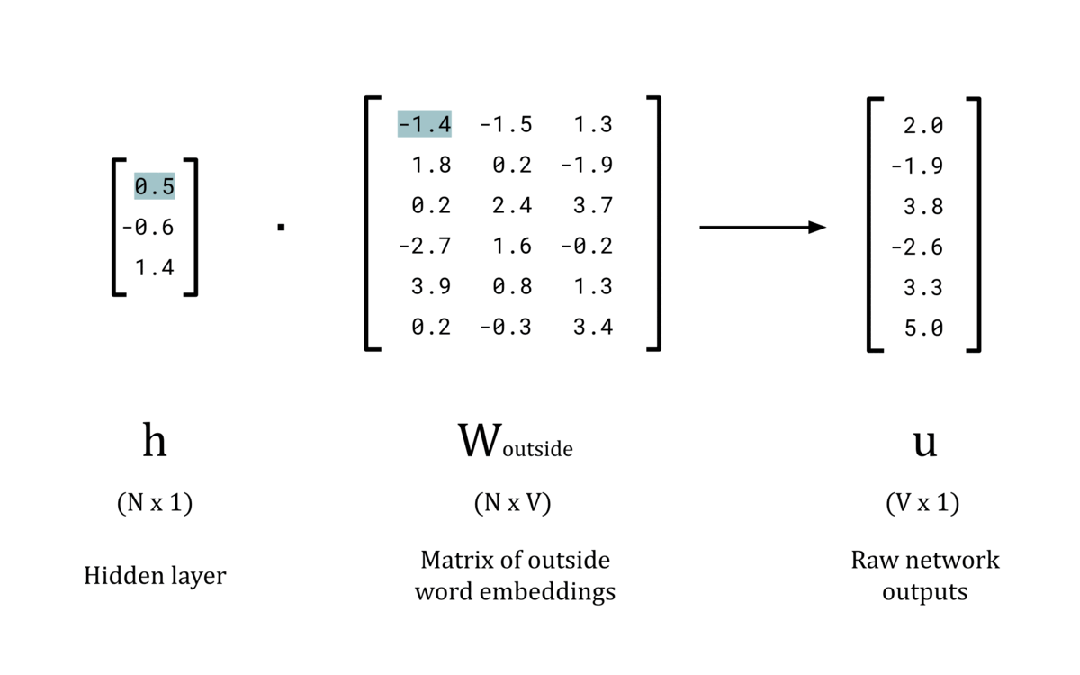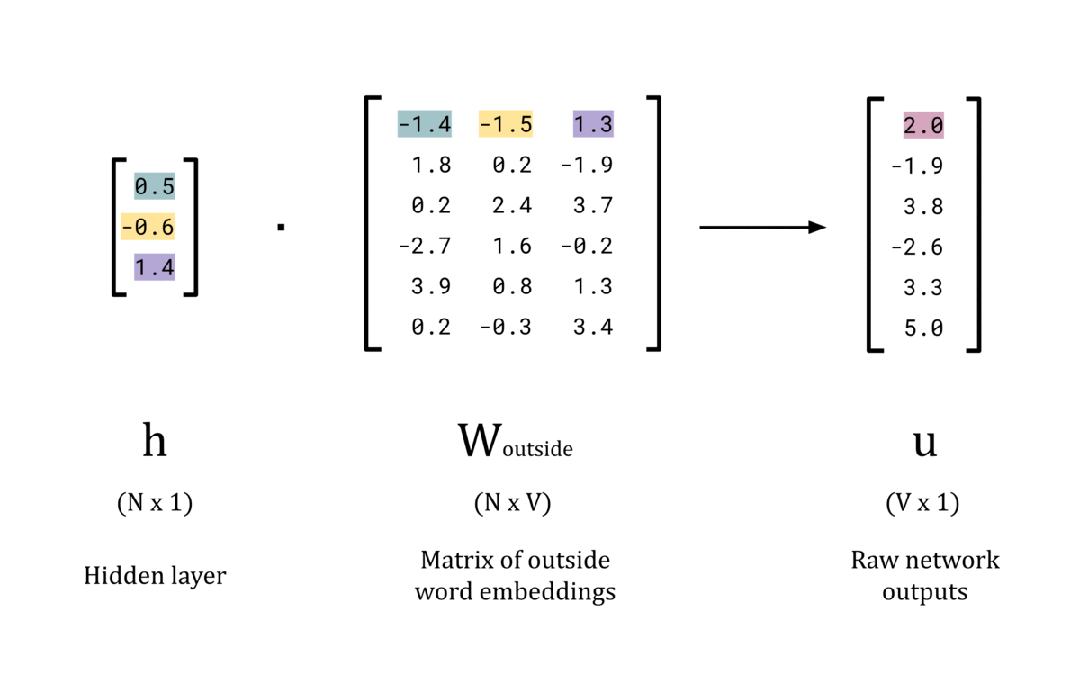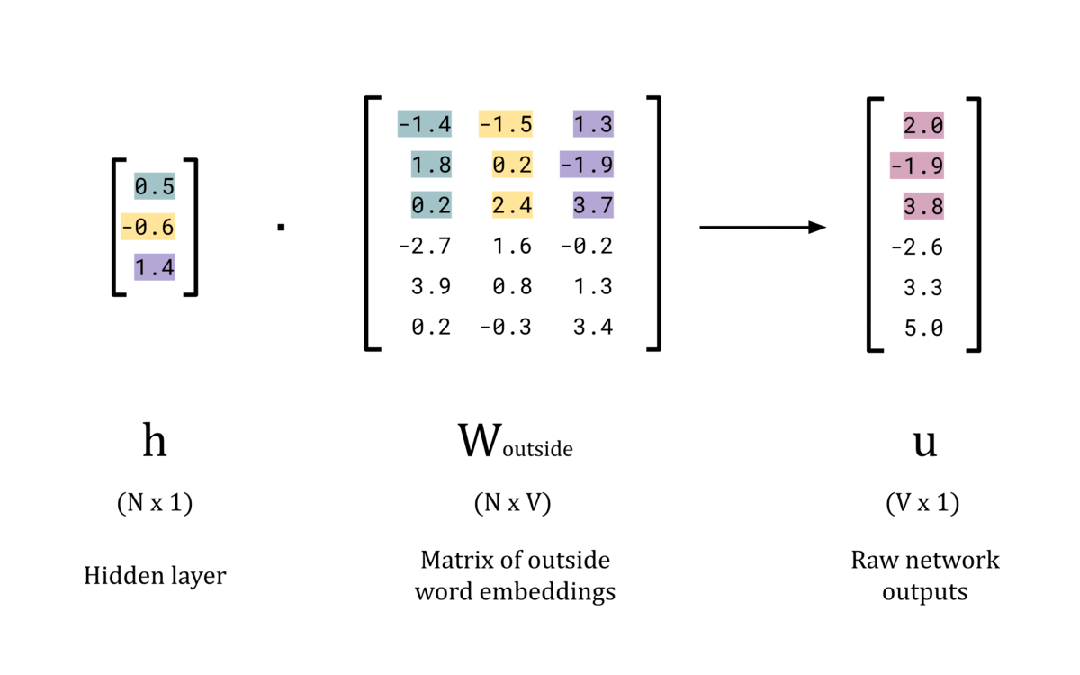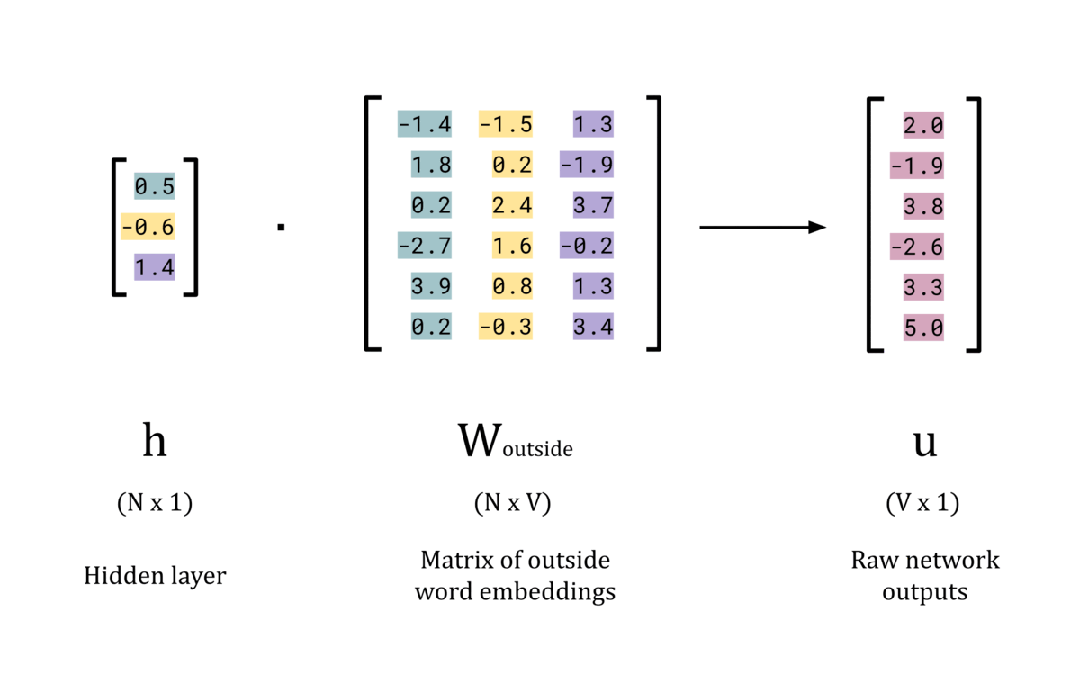
# Calculate the raw network outputs
w_outside = np.random.rand(EMBEDDING_DIM, vocab_size)
u = np.dot(h, w_outside)
# Print the results
print(f'Hidden layer, h: {h}n')
print(f'W_outside: nn{w_outside}n')
print(f'Raw network outputs (logits), u: {u}n')每个元素的值对应于一个单词属于给定中心词 x 的集合外部单词的“概率” 。
-
def softmax(u):
""" Return the softmax values for a vector u."""
values = np.exp(u)/np.sum(np.exp(u))
return values
def find_outside_words(y_pred, vocab):
# Get a sorted list of softmax scores
sorted_y_pred = y_pred.copy()
sorted_y_pred = sorted_y_pred[::-1]
top_score = sorted_y_pred[:1]
index = np.where(y_pred == top_score)[0][0]
print(index)
word = vocab[index]
return word
# Calculate the softmax outputs
y_pred = softmax(u)
outside_word = find_outside_words(y_pred, vocab)
# Print the results
print(f'Raw network outputs (logits), u: {u}n')
print(f'Softmax outputs, y_pred: {y_pred}n')
print(f'Outside words: {outside_word}')
综合比较
适用场景
性能
资源消耗